These docs are for Cribl Edge 4.1 and are no longer actively maintained.
See the latest version (4.16).
Splunk TCP
Cribl Edge supports receiving Splunk data from Universal or Heavy Forwarders.
Type: Push | TLS Support: YES | Event Breaker Support: YES
Configuring Cribl Edge to Receive Splunk TCP Data
From the top nav, click Manage, then select a Fleet to configure. Next, you have two options:
To configure via the graphical QuickConnect UI, click Routing > QuickConnect (Stream) or Collect (Edge). Next, click Add Source at left. From the resulting drawer’s tiles, select [Push > ] Splunk > Splunk TCP. Next, click either Add Destination or (if displayed) Select Existing. The resulting drawer will provide the options below.
Or, to configure via the Routing UI, click Data > Sources (Stream) or More > Sources (Edge). From the resulting page’s tiles or left nav, select [Push > ] Splunk > Splunk TCP. Next, click New Source to open a New Source modal that provides the options below.
Cribl Edge ships with a Splunk TCP Source preconfigured to listen on Port 9997. You can clone or directly modify this Source to further configure it, and then enable it.
General Settings
Input ID: Enter a unique name to identify this Splunk Source definition.
Address: Enter hostname/IP to listen for Splunk data. E.g., localhost or 0.0.0.0.
Port: Enter port number.
Optional Settings
Tags: Optionally, add tags that you can use for filtering and grouping in Cribl Edge. Use a tab or hard return between (arbitrary) tag names.
TLS Settings (Server Side)
Enabled defaults to No. When toggled to Yes:
Certificate name: Name of the predefined certificate.
Private key path: Server path containing the private key (in PEM format) to use. Path can reference $ENV_VARS.
Passphrase: Passphrase to use to decrypt private key.
Certificate path: Server path containing certificates (in PEM format) to use. Path can reference $ENV_VARS.
CA certificate path: Server path containing CA certificates (in PEM format) to use. Path can reference $ENV_VARS.
Authenticate client (mutual auth): Require clients to present their certificates. Used to perform mutual authentication using SSL certs. Defaults to No. When toggled to Yes:
Validate client certs: Reject certificates that are not authorized by a CA in the CA certificate path, or by another trusted CA (e.g., the system’s CA). Defaults to
No.Common name: Regex matching subject common names in peer certificates allowed to connect. Defaults to
.*. Matches on the substring afterCN=. As needed, escape regex tokens to match literal characters. E.g., to match the subjectCN=worker.cribl.local, you would enter:worker\.cribl\.local.
Minimum TLS version: Optionally, select the minimum TLS version to accept from connections.
Maximum TLS version: Optionally, select the maximum TLS version to accept from connections.
Persistent Queue Settings
In this section, you can optionally specify persistent queue storage, using the following controls. This will buffer and preserve incoming events when a downstream Destination is down, or exhibiting backpressure.
On Cribl-managed Cribl.Cloud Workers (with an Enterprise plan), this tab exposes only the Enable Persistent Queue toggle. If enabled, PQ is automatically configured in
Always Onmode, with a maximum queue size of 1 GB disk space allocated per Worker Process.
Enable Persistent Queue: Defaults to No. When toggled to Yes:
Mode: Select a condition for engaging persistent queues.
Always On: This default option will always write events to the persistent queue, before forwarding them to Cribl Edge’s data processing engine.Smart: This option will engage PQ only when the Source detects backpressure from Cribl Edge’s data processing engine.
Max buffer size: The maximum number of events to hold in memory before reporting backpressure to the Source. Defaults to 1000.
Commit frequency: The number of events to send downstream before committing that Stream has read them. Defaults to 42.
Max file size: The maximum data volume to store in each queue file before closing it and (optionally) applying the configured Compression. Enter a numeral with units of KB, MB, etc. If not specified, Cribl Edge applies the default 1 MB.
Max queue size: The maximum amount of disk space that the queue is allowed to consume, on each Worker Process. Once this limit is reached, Cribl Edge will stop queueing data, and will apply the Queue-full behavior. Enter a numeral with units of KB, MB, etc. If not specified, the implicit 0 default will enable Cribl Edge to fill all available disk space on the volume.
Queue file path: The location for the persistent queue files. Defaults to $CRIBL_HOME/state/queues. To this field’s specified path, Cribl Edge will append /<worker-id>/inputs/<input-id>.
Compression: Optional codec to compress the persisted data after a file is closed. Defaults to None; Gzip is also available.
As of Cribl Edge 4.1, Source-side PQ’s default Mode changed from
SmarttoAlways on. This option more reliably ensures events’ delivery, and the change does not affect existing Sources’ configurations. However:
- If you create Stream Sources programmatically, and you want to enforce the previous
Smartmode, you’ll need to update your existing code.- If you enable
Always on, this can reduce data throughput. As a trade-off for data durability, you might need to either accept slower throughput, or provision more machines/faster disks.- You can optimize Workers’ startup connections and CPU load at Fleet Settings > Worker Processes.
Processing Settings
Event Breakers
Event Breakers are applied only to raw, unparsed data. Data originating from Splunk Heavy Forwarders or Universal Forwarders with sourcetypes configured for event breaking or indexed extractions bypasses Event Breakers, as it is already segmented into discrete events.
Event Breaker rulesets: A list of event breaking rulesets that will be applied to the input data stream before the data is sent through the Routes. Defaults to System Default Rule.
Event Breaker buffer timeout: How long (in milliseconds) the Event Breaker will wait for new data to be sent to a specific channel, before flushing out the data stream, as-is, to the Routes. Minimum 10 ms, default 10000 (10 sec), maximum 43200000 (12 hours).
Fields
In this section, you can add Fields to each event, using Eval-like functionality.
Name: Field name.
Value: JavaScript expression to compute field’s value, enclosed in quotes or backticks. (Can evaluate to a constant.)
Pre-Processing
In this section’s Pipeline drop-down list, you can select a single existing Pipeline to process data from this input before the data is sent through the Routes.
Auth Tokens
Add Token : Click to add authorization tokens. Each token’s section provides the fields listed below. If no tokens are specified, unauthenticated access will be permitted.
Token: Shared secrets to be provided by any Splunk forwarder (Authorization: <token>). Click Generate to create a new secret.
Description: Optional description of this token.
Advanced Settings
Enable Proxy Protocol: Toggle to Yes if the connection is proxied by a device that supports Proxy Protocol v1 or v2.
IP allowlist regex: Regex matching IP addresses that are allowed to establish a connection. Defaults to .* (i.e., all IPs).
Max active connections: Maximum number of active connections allowed per Worker Process. Defaults to 1000. Set a lower value if connection storms are causing the Source to hang. Set 0 for unlimited connections.
Max S2S version: The highest version of the Splunk-to-Splunk protocol to expose during handshake. Defaults to v3; v4 is also available.
Use Universal Forwarder time zone: Displayed (and enabled by default) only when Max S2S version is set to v4. Provides Event Breakers with a __TZ field, which derives events’ time zone from UF-provided metadata. See Using the UF Time Zone and Configuring a Splunk Forwarder, below.
Environment: If you’re using GitOps, optionally use this field to specify a single Git branch on which to enable this configuration. If empty, the config will be enabled everywhere.
Connected Destinations
Select Send to Routes to enable conditional routing, filtering, and cloning of this Source’s data via the Routing table.
Select QuickConnect to send this Source’s data to one or more Destinations via independent, direct connections.
Using the UF Time Zone
Under Advanced Settings, the Use Universal Forwarder time zone toggle mitigates cases where incoming events have timestamp strings but no time zone information. For example:
12-15-2022 14:57:22.080 WARN TcpOutputFd [1607 TcpOutEloop] - Connect to 172.17.0.1:9997 failed. Connection refusedThis gap can be problematic, especially if the originating Universal Forwarder is in a different time zone from the processing Edge Node.
The __TZ field is the solution. Event Breakers use the __TZ field to derive time zone information, enabling them to set the _time field correctly. Derived time zone information will appear in Cribl Edge’s own logs as shown below:
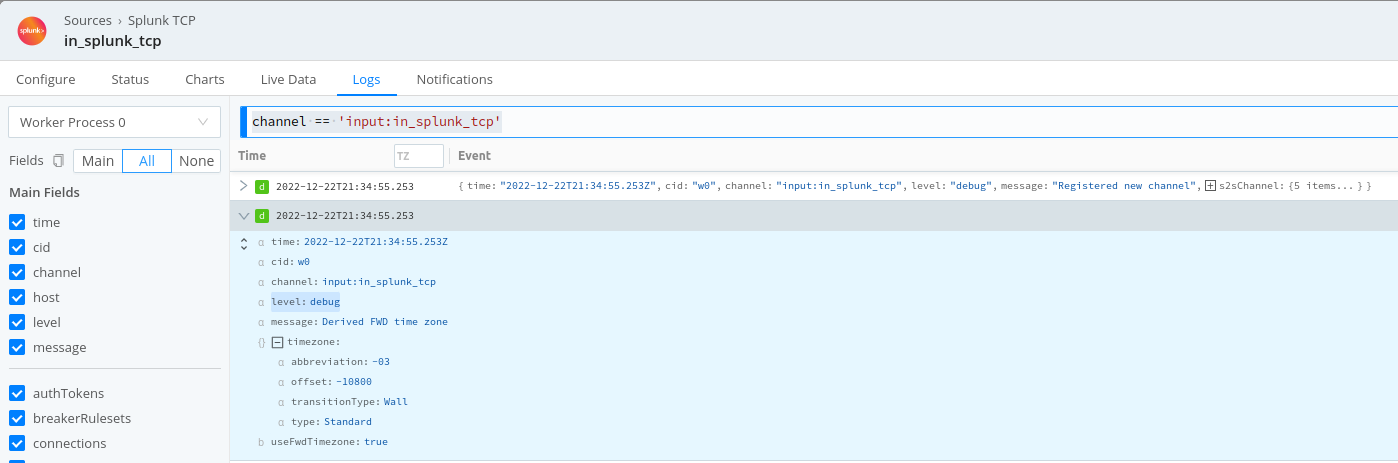
Internal Fields
Cribl Edge uses a set of internal fields to assist in handling of data. These “meta” fields are not part of an event, but they are accessible, and Functions can use them to make processing decisions.
Fields for this Source:
__inputId__s2sVersion- value can be eitherv3orv4__source__srcIpPort__TZ- see above
Configuring a Splunk Forwarder
To configure a Splunk forwarder (UF, HF) use the following sample outputs.conf stanzas:
[tcpout]
disabled = false
defaultGroup = cribl, <optional_clone_target_group>, ...
[tcpout:cribl]
server = [<cribl_ip>|<cribl_host>]:<port>, [<cribl_ip>|<cribl_host>]:<port>, ...
sendCookedData = true
# As of Splunk 6.5, using forceTimebasedAutoLB is no longer recommended. Ensure this is left at default for UFs
# forceTimebasedAutoLB = false
negotiateProtocolLevel = 0[tcpout]
disabled = false
defaultGroup = cribl
[tcpout:cribl]
server = in.main-default-<Your-Org-ID>.cribl.cloud:9997
# sslVerifyServerCert = true
sslRootCAPath = $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/auth/cacert.pem
useSSL = true
sendCookedData = true
negotiateProtocolLevel = 0Preventing Data Loss with v3
If you set Max S2S version to
v3, Cribl recommends that you use thenegotiateProtocolLevel = 0setting shown above to avoid data loss. Depending on your environment, enablingnegotiateProtocolLevelwith a non-0value could cause Cribl Edge to not accept data from the forwarder.If you set Max S2S version to
v4, this setting is not necessary. The Splunk receiver will detect which version is in use and automatically use the correct handler.See Internal Fields for information on the
__s2sVersionfield.
Troubleshooting Splunk Forwarder Performance Issues
If you encounter performance issues with a Splunk Forwarder, Cribl recommends increasing the number of parallel ingestion Pipelines or increasing forwarder throughput. You can experiment with either or both of these settings.
To increase the number of parallel ingestion Pipelines, adjust the setting for parallelIngestionPipelines in server.conf. Experiment with values ranging from 2-4.
To adjust forwarder throughput, increase the maxKBps value in limits.conf. The default value is 256. A value of 0 removes all throttling from the forwarder.





