These docs are for Cribl Edge 4.3 and are no longer actively maintained.
See the latest version (4.16).
Kubernetes Logs
The Kubernetes Logs Source collects logs from containers on a Kubernetes node. Optionally, you can filter and enrich incoming logs. You must authorize this Source to access the Pods in all namespaces. For details, see RBAC for Kubernetes Logs Source.
Type: System and Internal | TLS Support: N/A | Event Breaker Support: Yes | Uses Key-Value Store
Cribl Edge supports configuring only one Kubernetes Logs Source per Edge Node and per Fleet. This Source is currently unavailable on Cribl-managed Cribl.Cloud Workers.
Discovering and Filtering Kubernetes Pods to Monitor
The Kubernetes Logs Source connects to the Kubernetes API and loads the lists of Pods on the node, on a configurable Polling interval. The Source then runs the Pods through the Filter Rules to determine which ones to report on.
If no rules are configured, or if all of the rules evaluate to true, the Source generates logs for the Pod’s containers. Conversely, if any of the rules evaluate to false, the Source skips the Pod’s containers, and does not generate any logs for it.
Cluster/Daemonset Best Practices
For the Kubernetes Logs Source to work as designed, Cribl recommends deploying Cribl Edge as a Daemonset. For details, see Deploying via Kubernetes.
This Source will refuse to run when it connects to the cluster API instead of to the kubelet on the local node. This happens when you run Cribl Edge outside of the cluster; or when you deploy it inside the cluster, but in a way that it can’t detect the local Pod/node. In these cases, Edge will emit an error when it initializes this Source.
You can bypass the error state by setting the
CRIBL_K8S_FOOTGUNenvironment variable totrue. However, you will assume the risk that the Kubernetes Logs Source might make excessive calls to the cluster API.
Configuring Cribl Edge to Collect Kubernetes Logs
From the top nav, click Manage, then select a Fleet to configure. Then, you have two options:
To configure via the graphical QuickConnect UI, click Collect. By default, a Kubernetes Logs tile appears at left. Hover over it and select Configure to open a drawer that provides the options below.
To configure via the Routing UI, click More > Sources. From the resulting page’s tiles or the Sources left nav, select System and Internal > Kubernetes Logs. Next, click the default
in_kube_logsSource to open a modal that provides the options below.
General Settings
Input ID: This is prefilled with the default value in_kube_logs, which cannot be changed via the UI, due to the single-Source restrictions above.
Optional Settings
Polling interval: How often, in seconds, to collect metrics. If not specified, defaults to 15 seconds.
Filter Rules: Optionally, specify the Kubernetes Pods that this Source should parse to generate logs. If you specify no restrictive rules here, the Source will emit all events.
- Filter expression: JavaScript expression to filter Kubernetes Pod objects. Filters are based on the Kubernetes Pod Object definition, and evaluated from top to bottom. The first expression evaluating to
falseexcludes the Pod from collection. The default filter is!metadata.namespace.startsWith('kube-'), which ignores Pods in the kube-* namespace.
Other Filter expressions examples include:
Collect logs from Pods on a specific Node -
spec.nodeName == 'node1'Ignore all DaemonSets -
metadata.ownerReferences[0].kind != 'DaemonSet'Ignore Pods with specific Container names -
spec.containers[0].name != 'edge'Description: Optional description of the rule.
Pods are either included or excluded entirely based on the Filter Rules.
Enable timestamps: When toggled to Yes, Cribl Edge prefixes a timestamp to each line of the container’s raw console output. When you enable timestamps, you must select the kubernetes_logs pre-processing Pipeline. This Pipeline removes conflicting timestamps prepended by the Source. This combination is designed for working with containers whose console output lacks proper timestamps (either because the timestamps are missing altogether or because they specify time only but not date).
Tags: Optionally, add tags that you can use to filter and group Sources in Cribl Edge’s Manage Sources page. These tags aren’t added to processed events. Use a tab or hard return between (arbitrary) tag names.
Processing Settings
Event Breakers
This section defines event breaking rulesets that will be applied, in order, on the /raw endpoint.
Event Breaker rulesets: A list of event breaking rulesets that will be applied to the input data stream before the data is sent through the Routes. Defaults to System Default Rule.
Event Breaker buffer timeout: How long (in milliseconds) the Event Breaker will wait for new data to be sent to a specific channel, before flushing out the data stream, as-is, to the Routes. Minimum 10 ms, default 10000 (10 sec.), maximum 43200000 (12 hours).
Fields
In this section, you can add Fields to each event using Eval-like functionality.
Name: Field name.
Value: JavaScript expression to compute field’s value, enclosed in quotes or backticks. (Can evaluate to a constant.)
Pre-Processing
Select a Pipeline (or Pack) from the drop-down to process this Source’s data. Required to configure this Source via Data Routes; optional to configure via Collect/QuickConnect.
Advanced Settings
Environment: If you’re using GitOps, optionally use this field to specify a single Git branch on which to enable this configuration. If empty, the config will be enabled everywhere.
Connected Destinations
Select Send to Routes to enable conditional routing, filtering, and cloning of this Source’s data via the Routing table.
Select QuickConnect to send this Source’s data to one or more Destinations via independent, direct connections.
Internal Fields
Cribl Edge uses a set of internal fields to assist in forwarding data to a Destination.
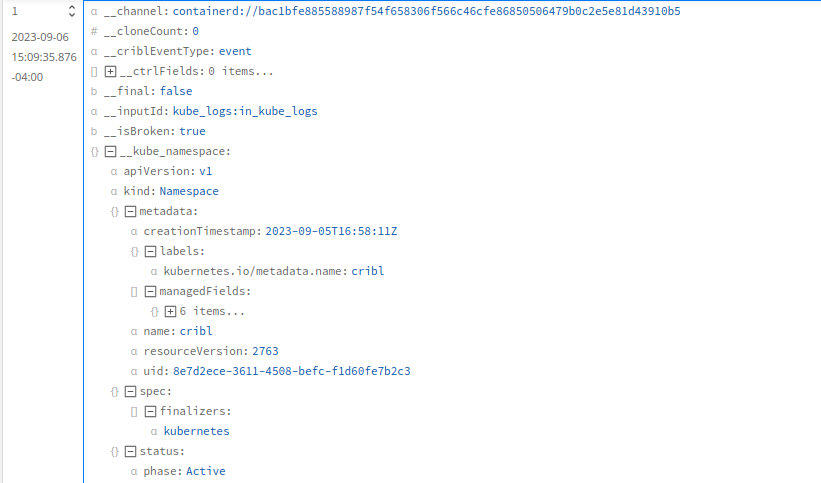
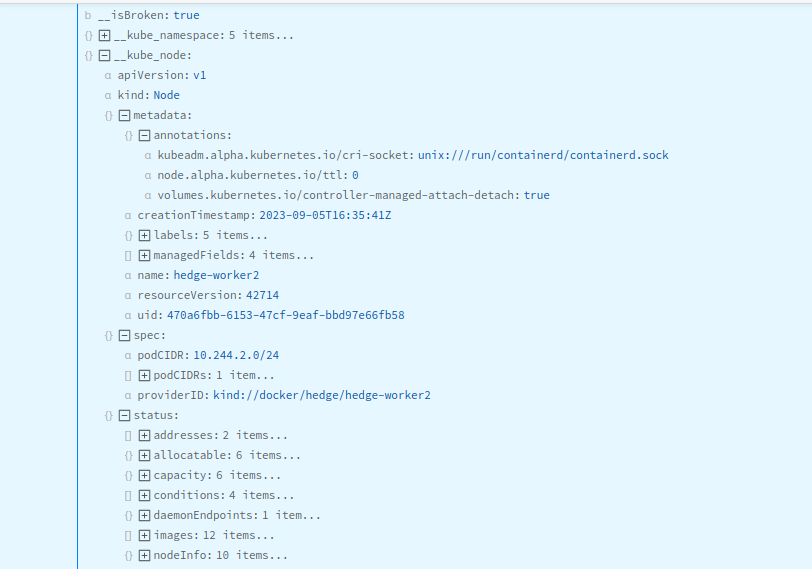
These are the full objects from the Kubernetes API, showing the namespace, node, and Pod where the log originated:
__channel__extractedTime__final__isBroken__kube_namespace__kube_node__kube_pod__raw__source_raw_time
For details, see Objects in Kubernetes.
Key-Value Store
The Kubernetes Logs Source uses key-value store for container information. Container IDs are used as.
Sample Log Event
The following screenshots show the __kube objects corresponding to a sample log event.
Namespace Metadata
Node Metadata
Pod Metadata






