These docs are for Cribl Edge 4.7 and are no longer actively maintained.
See the latest version (4.16).
Monitoring Health and Metrics
To get an operational view of your Cribl Edge deployment, consult the following resources.
Landing Pages
When you first log into your Distributed Deployment, you will be greeted with tiles prompting you to choose a product. The Cribl Edge tile displays basic configuration details, including number of Fleets, Subfleets, Edge Nodes, and events and bytes over time.
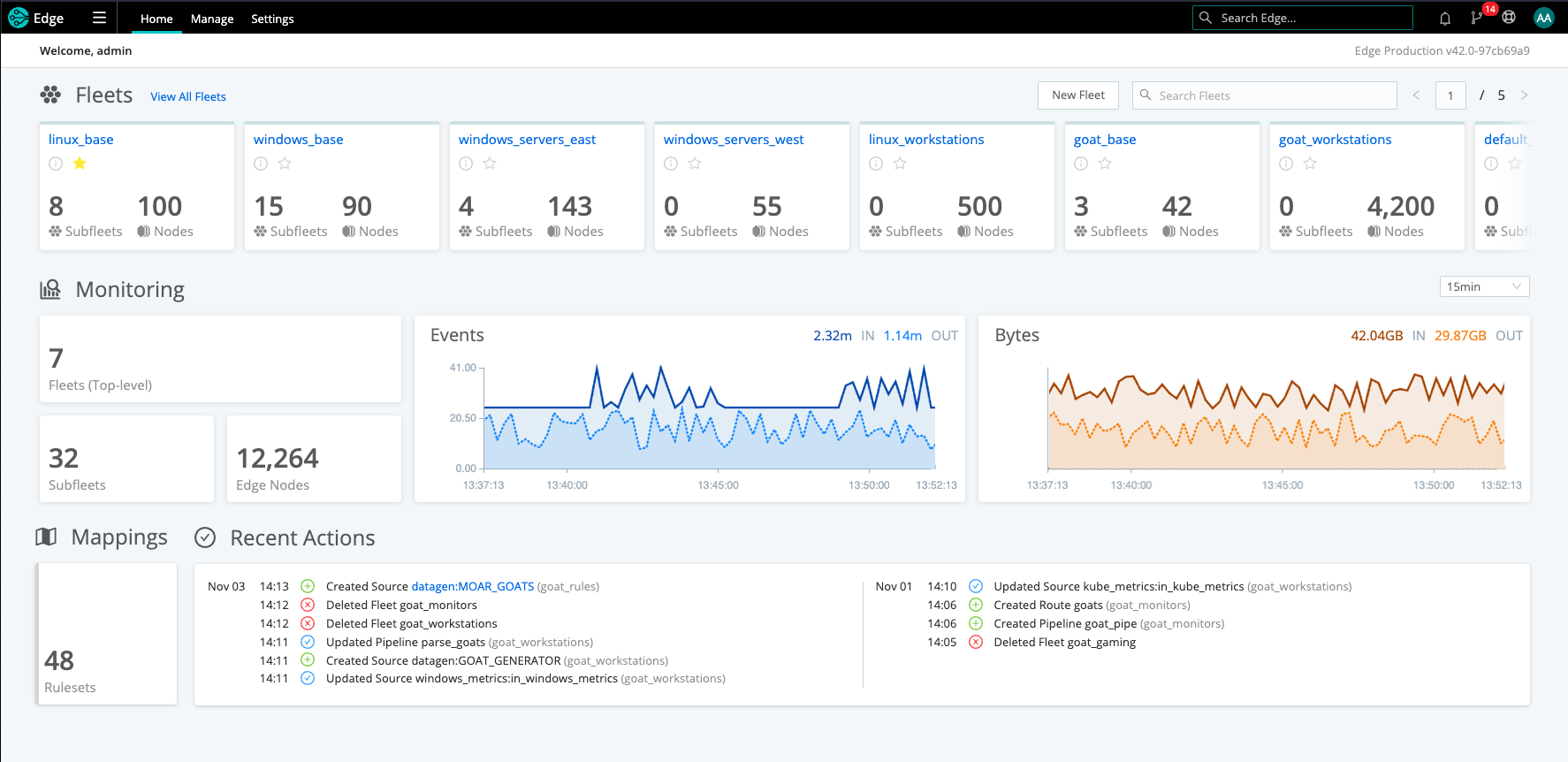
Select Manage to navigate to the Cribl Edge Home page, which shows aggregate data for all Fleets, Subfleets and Edge Nodes. The charts display information about traffic in and out of the system.
On top of the Bytes chart, you can change the display’s granularity from the default last 5 min, selecting a variety of time ranges from 1 min up to 1 day (covering the preceding 24 hours).
Select Manage from the top nav to view the Fleets Landing page. Here you can access the tabs for more information about your Fleets (and Subfleets), Edge Nodes, Mappings, Notifications, and Logs.
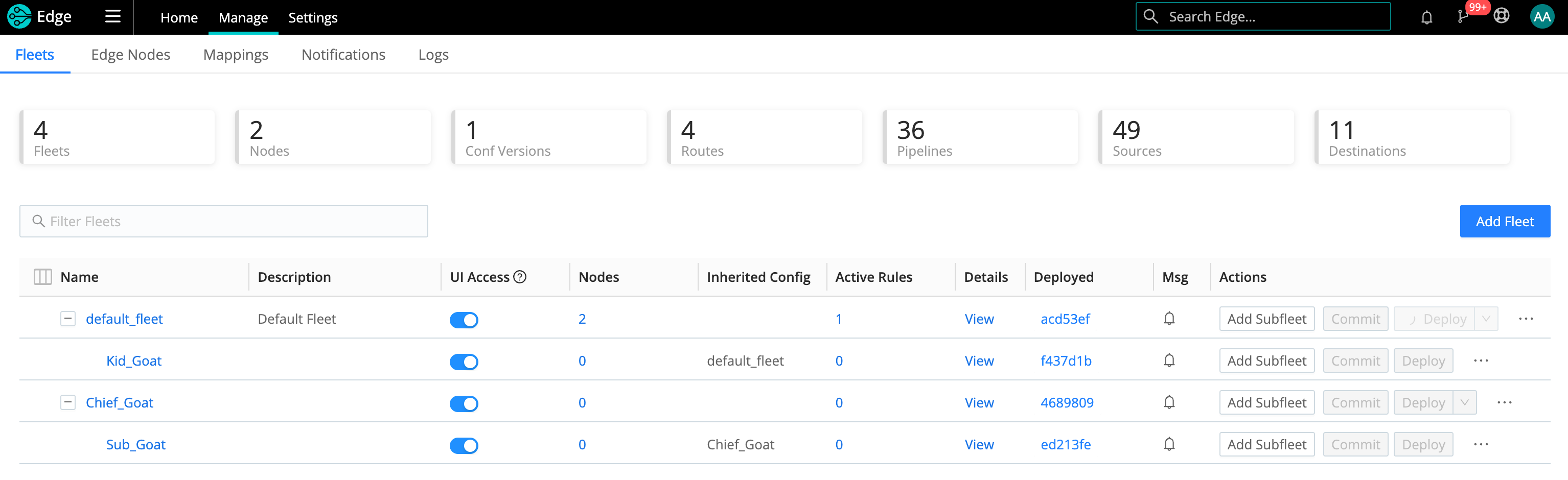
The Manage Fleets page gives you access to more information about your Fleets (and Subfleets), Edge Nodes, Mappings, Notifications, and Logs.
You can click a Fleet link to isolate individual Fleets, or use the Search bar to locate your Fleet.
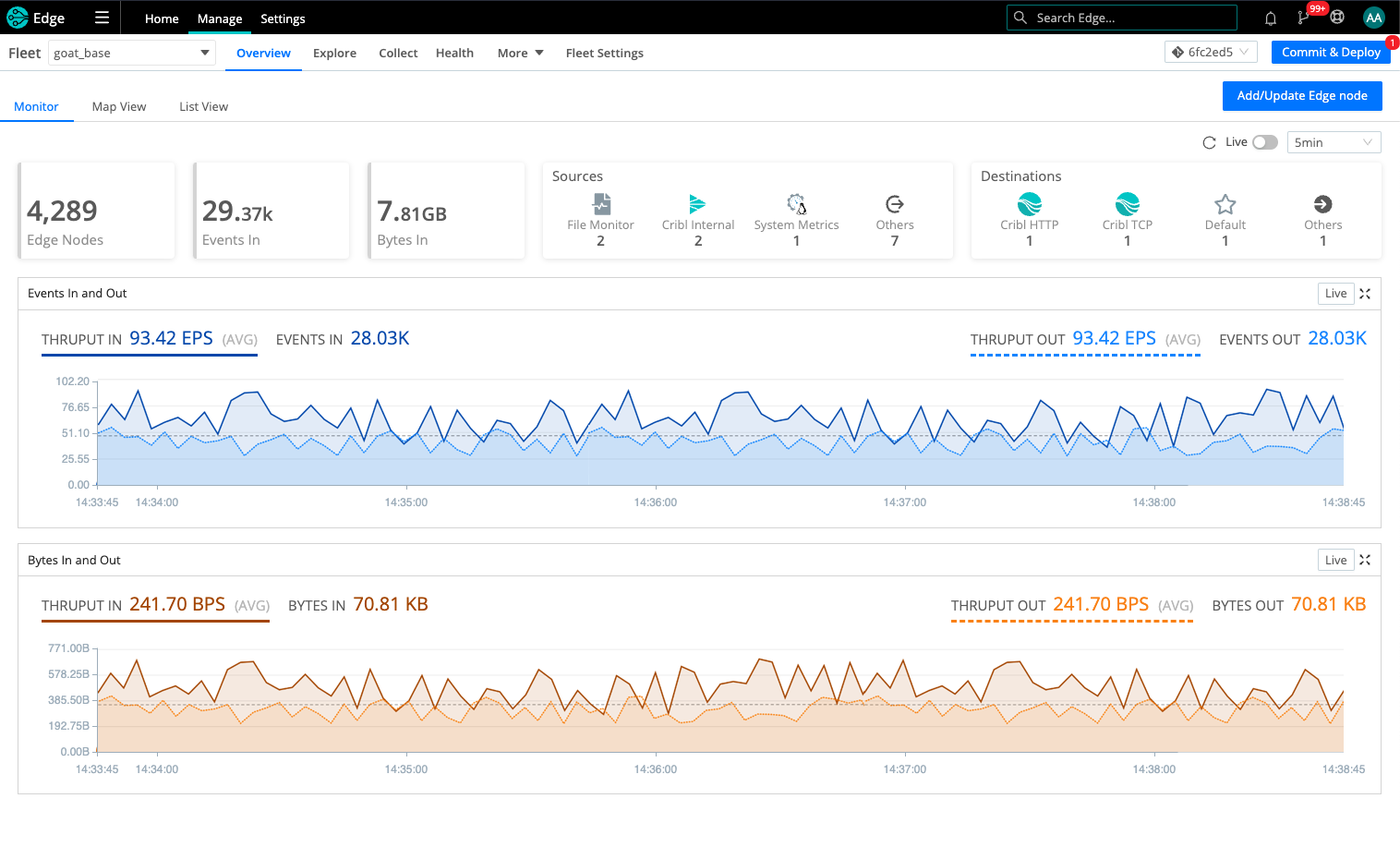
Source and Destination Health Status
When you add or manage configured Sources and Destinations, you’ll see a colored health status (if enabled). In the list view, this status is a green, orange, red, or gray dot next to the name, along with a gray circle indicating the number of instances you have configured.
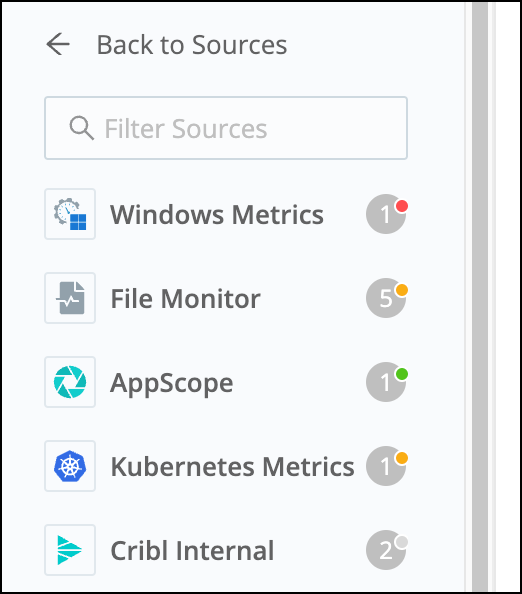
In the tile view, colors are applied to the squares that indicate the number of instances you have configured.

The colors have the following meanings for each Source and Destination:
- Green: Working properly
- Orange: Experiencing problems
- Red: Experiencing severe problems
- Gray: Not enabled
To learn more about the health status of any Source or Destination, click its name to open the list of existing Sources or Destinations, and then click the Status icon for the one you want to examine.
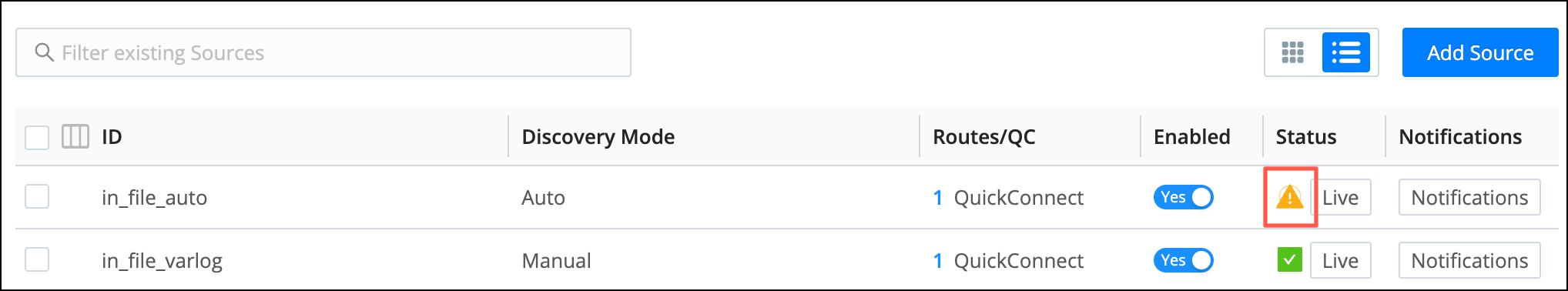
In the modal that opens, click the Status icon again to see more details.
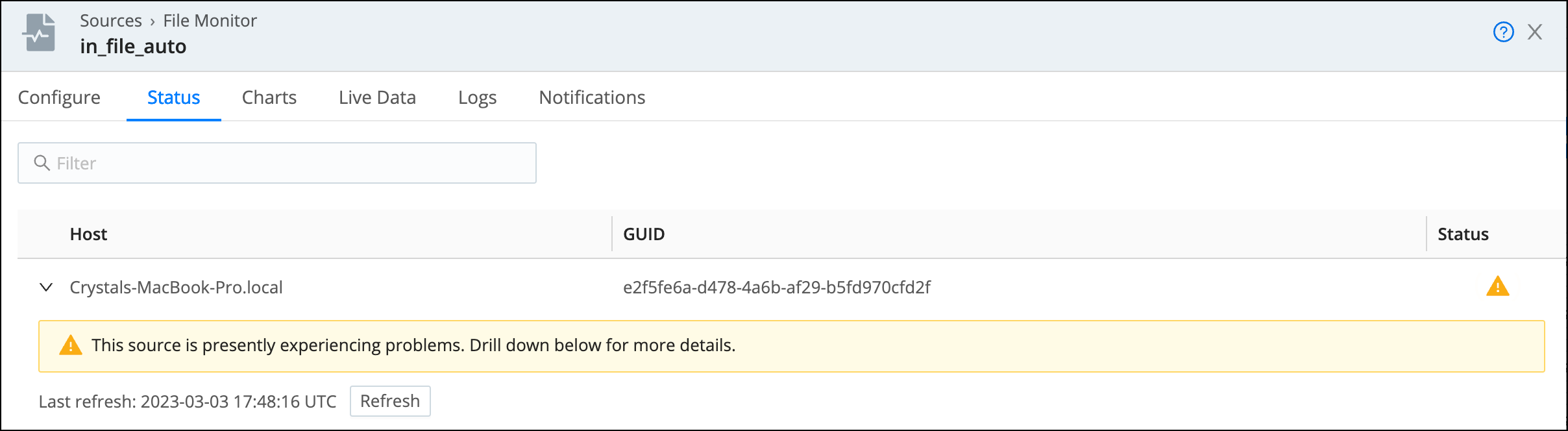
When there are more than 100 Nodes in the Fleet, the Status column will not be visible in the list of Nodes. To view the status for an individual Node, expand it in the list. You can only expand one Node at a time. Refresh the list of Nodes and their status with the Refresh button.
Enabling Health Status
Health status must be enabled independently for each fleet in Fleet Settings. To enable health status for a Fleet:
- Select the Fleet you want to manage.
- On the Manage page, select the Fleet Settings tab.
- Navigate to General Settings > Limits > Metrics.
- Under Metrics to send from Edge Nodes, use the buttons to select or create a set of metrics.
If Minimal is selected, health status will not be enabled for the Fleet and health icons will appear white for all Sources and Destinations.
To learn more about these metrics options, see Controlling Metrics.
Health Status
You can isolate throughput for any of the following:
- Sources
- Destinations
- Routes
- Pipelines
- Packs
- Data Fields (Edge Nodes only)
For Fleets, go to the Health tab and click the tab you want. For Edge Nodes, go to the Edge Node’s Health tab, and then select an option on the Data submenu.
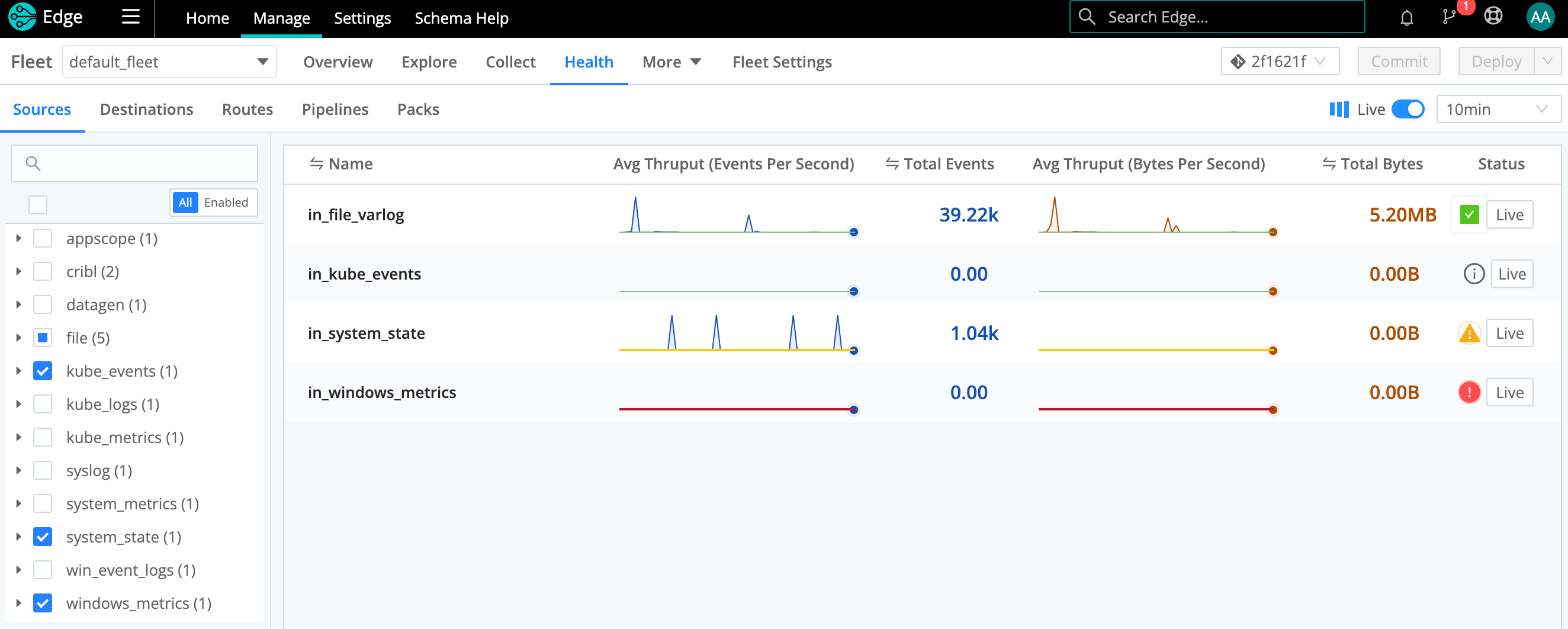
Dense displays are condensed to sparklines for legibility.
The Status column displays the health of each resource with a colored icon. Click the icon to see more details. If a Fleet’s Health tab is empty, health status might not be enabled because only minimal metrics are being sent. You can enable health status by going to Fleet Settings > General Settings > Metrics and selecting Basic or All under Metrics to send from Edge Nodes. See Controlling Metrics to learn more about these options.
Hover over the right edge to display Maximize buttons that you can click to zoom these up to detailed graphs.
You can hover over an expanded graph fly-out to display further details.
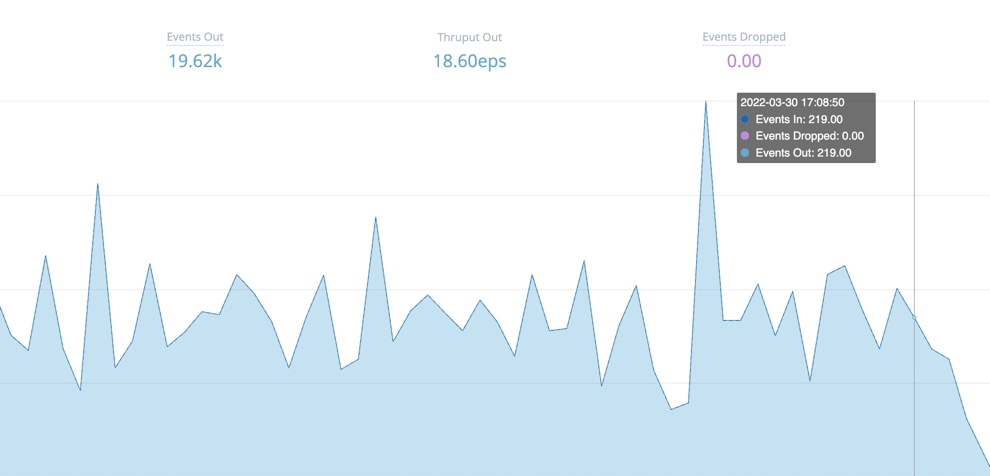
Edge Node Health
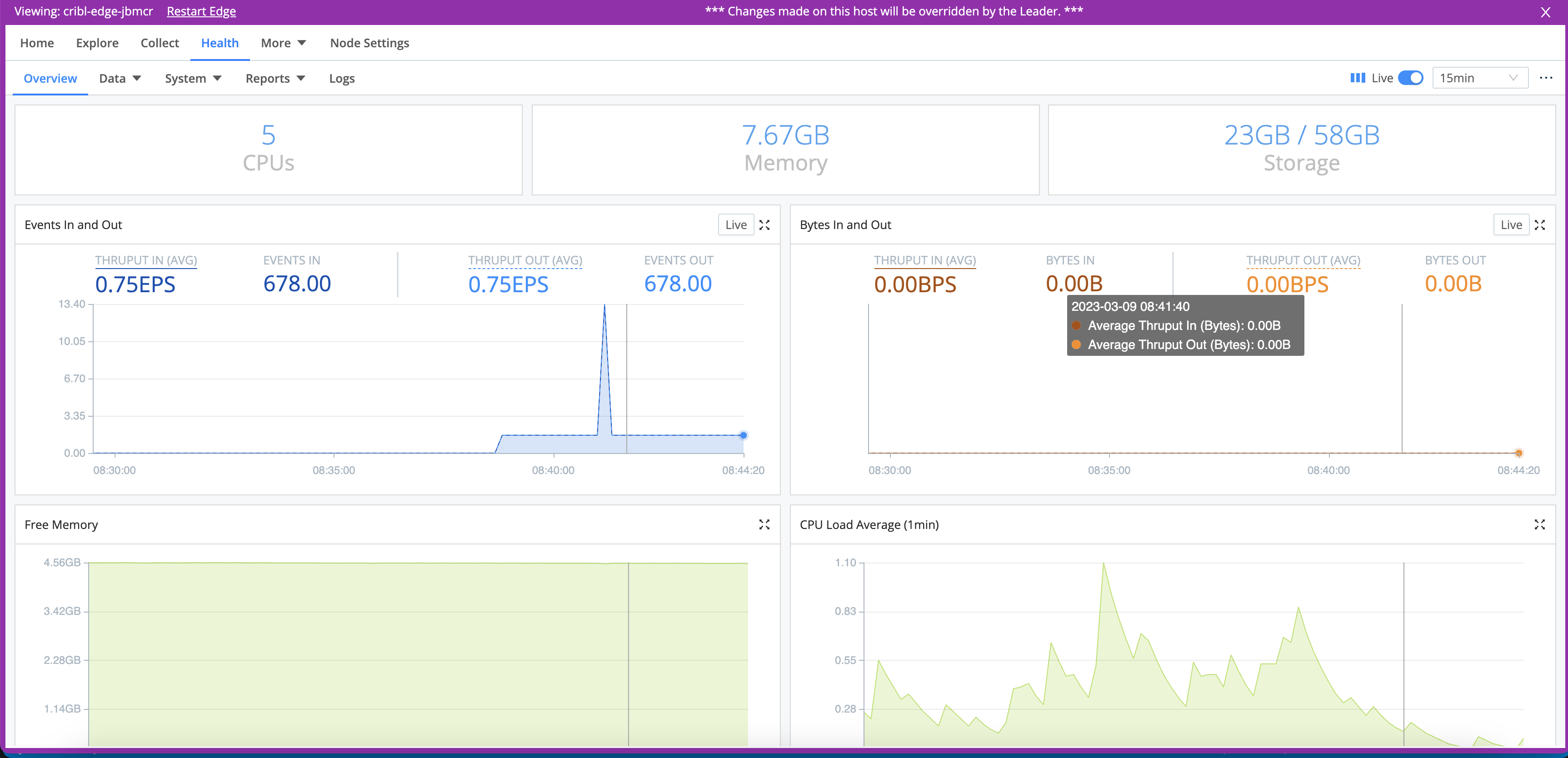
To review the health status of an Edge Node, teleport into the Node. From the Fleet landing page, click the List View tab, and then click the Edge Node GUID link to teleport from the Leader into the Edge Node. From the top nav of the Edge Node, click the Health tab for monitoring details.
Metrics are displayed in the Cribl Edge UI in units of KB, MB, GB, and TB. At each level, these are multiples of
1024.
The displayed Storage represents the amount of free storage remaining on the partition where Cribl Stream is installed. (This quantity might not represent the maximum storage available for the selected Edge Node or Fleet. Also, it does not calculate the system free space.)
Similarly, the Free Memory graph reflects only the operating system’s free statistic, matching Linux’s strict free definition by excluding buff/cache memory. So this graph indicates a lower value than the OS’ available memory statistic - and it does not necessarily indicate that the OS is running out of memory to allocate.
Byte-related charts show the uncompressed amounts and rates of data processed over the selected time range:
- Events (total) in and out
- Events per second in and out
- Bytes (total) in and out
- Bytes per second in and out
We measure bytes in and out based on the size of _raw, if this field is present and is of type string. Otherwise, we use the size of read (uncompressed) data.
The displayed CPU Load Average is an average Edge Node Process, updated at 1-minute granularity. (It is not an average for the Edge Node as a whole.)
Monitoring data does not persist across Cribl Edge restarts. Keep this in mind before you restart the server.
System Monitoring
From the Health page’s top nav, open the System submenu to isolate throughput for:
- Queues (Sources)
- Queues (Destinations)
For details, see Persistent Queues.
Reports/Top Talkers
Select Health > Reports / Top Talkers > Top Talkers, where you can examine your five highest-volume Sources, Destinations, Pipelines, Routes, and Packs. All components are ranked by events throughput. Sources and Destinations get separate rankings by bytes in and out, respectively.
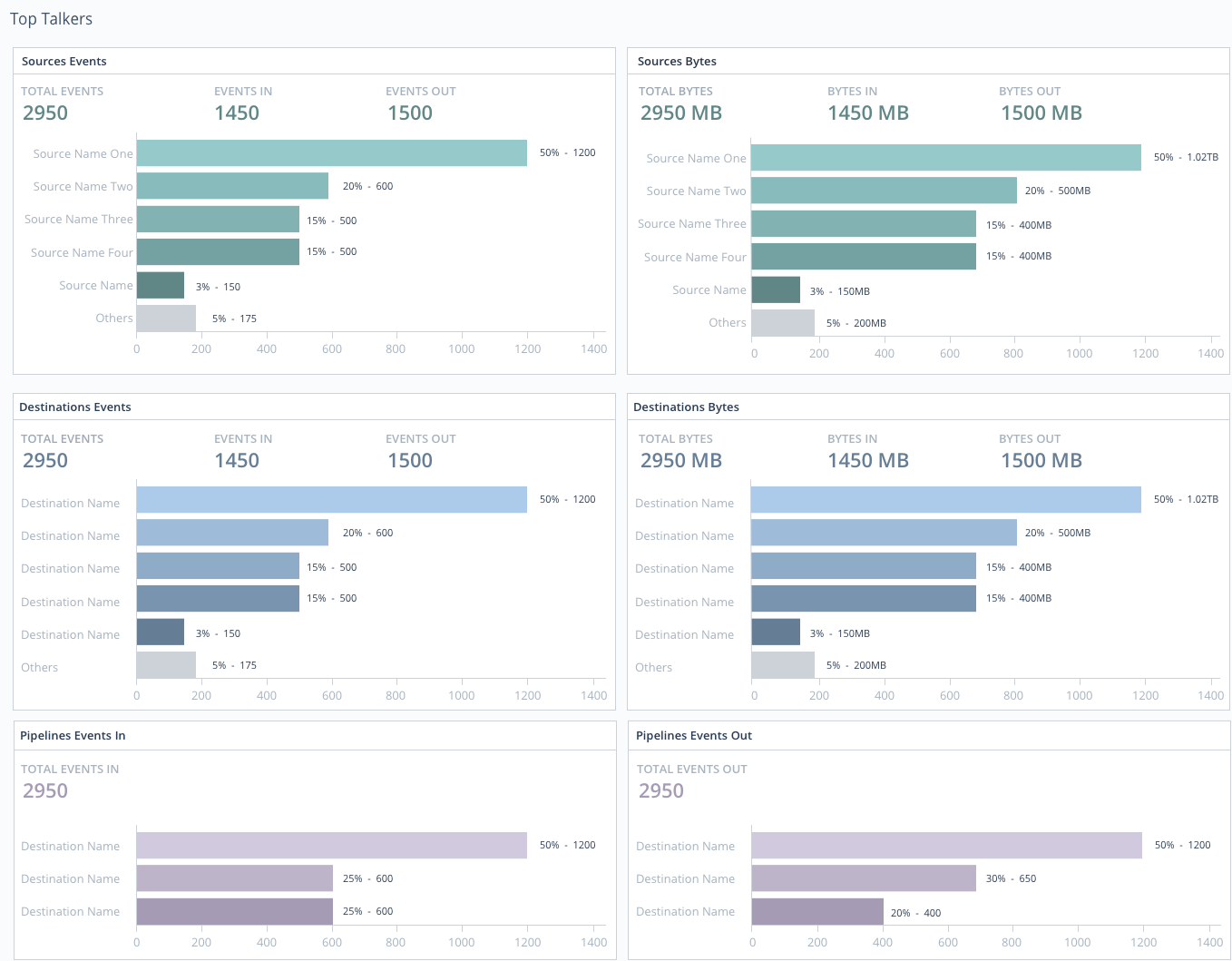
Internal Logs and Metrics
Select Logs from the Health page’s top nav. Cribl Edge’s internal logs and internal metrics provide comprehensive information about an instance’s status/health, inputs, outputs, Pipelines, Routes, Functions, and traffic.
Health Endpoint
Each Cribl Edge instance exposes a /health endpoint that is commonly used along with a Load Balancer to support operational decision-making. See Leader High Availability/Failover: Load Balancers for more information.
For many HTTP-based Sources, you can enable a Source-level health check endpoint in the Advanced Settings tab. The request URL format for these endpoints is
http(s)://${hostName}:${port}/cribl_health. Refer to the configuration instructions for a Source to learn whether the health check endpoint is available for it.
Types of Logs
Cribl Edge provides the following log types, by originating process:
API Server Logs - These logs are emitted primarily by the
API/mainprocess. They correspond to the top-levelcribl.logthat shows up on the Diag page. These include telemetry/license-validation logs. Filesystem location:$CRIBL_HOME/log/cribl.logEdge Node Process(es) Logs - These logs are emitted by all the Edge Node Processes, and are very common on single-instance deployments and Edge Nodes. Filesystem location:
$CRIBL_HOME/log/worker/N/cribl.logFleet Logs - These logs are emitted by all processes that help a Leader Node configure Fleets. Filesystem location:
$CRIBL_HOME/log/group/GROUPNAME/cribl.log
For details about generated log files, see Internal Logs. To work with logs in Cribl Edge’s UI, see Search Internal Logs.
Log Rotation and Retention
Cribl Edge rotates logs every 5 MB, keeping the most recent 5 logs. Logs will reach the 5 MB threshold more quickly with verbose logging settings (such as debug) and with high volumes of system activity. In a
Distributed deployment (Edge), all Edge Nodes
forward their metrics to the Leader Node, which then consolidates them to
provide a deployment-wide view.
For long-term retention, Cribl recommends sending logs from the Leader, and the Cribl Internal > CriblLogs Sources on Edge Nodes, to a downstream service of your choice. See the next section for details.
Forward Logs and Metrics Externally
Cribl Edge supports forwarding internal logs and metrics to your preferred external monitoring solution. To make internal data available to send out, go to More > Sources and enable the Cribl Internal Source.
This will send internal logs and metrics down through Routes and Pipelines, just like another data source. Both logs and metrics will have a field called source, set to the value cribl, which you can use in Routes’ filters.
Note that the only logs supported here are Edge Node Process logs (see Types of Logs above). You can, however, use a Script Collector to listen for API Server or Edge Node Fleet events.
For recommendations about useful Cribl metrics to monitor, see Internal Metrics.
CriblMetrics Override
The Disable field metrics setting - in Settings (top nav) > System > General Settings > Limits - applies only to metrics sent to the Leader Node. When the Cribl Internal Source is enabled, Cribl Edge ignores this Disable field metrics setting, and full-fidelity data will flow down the Routes.
Search Internal Logs
Cribl Edge exists because logs are great and wonderful things! Using Cribl Edge’s Health > Logs page, you can search all Cribl Edge’s internal logs at once - from a single location, for both Leader and Edge Node. This enables you to query across all internal logs for strings of interest.
The labels on this screenshot highlight the key controls you can use (see the descriptions below):
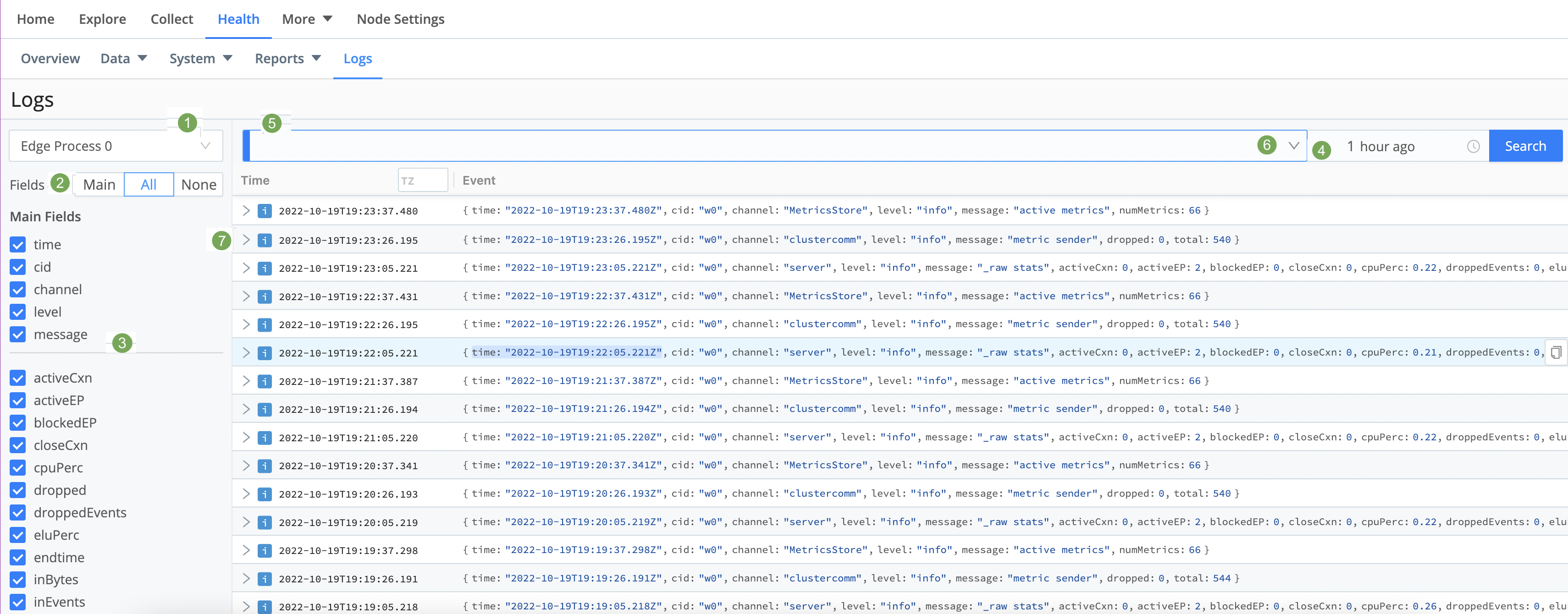
Log file selector: Choose the types of logs to view.
Fields selector: Click the Main | All | None toggles to quickly select or deselect multiple check boxes below. Beside these toggles, a Copy button enables you to copy field names to the clipboard in CSV format.
Fields: Select or deselect these check boxes to determine which columns are displayed in the Results pane at right. (The upper Main Fields group will contain data for every event; other fields might not display data for all events.)
Time range selector: Select a standard or custom range of log data to display. (The Custom Time Range pickers use your local time, even though the logs’ timestamps are in UTC.)
Search box: To limit the displayed results, enter a JavaScript expression here. An expression must evaluate to
truthyto return results. You can press Shift+Enter to insert a newline.
To modify the depth of information that is originally input to the Logs page, see Logging Settings.
Click the Search box’s history arrow (right side) to retrieve recent queries.
The Results pane displays most-recent events first. Each event’s icon is color-coded to match the event’s severity level.
Click individual log events to unwrap an expanded view of their fields.
Logging Settings
On Cribl Edge’s Settings pages, you can adjust the level (verbosity) of internal logging data processed, per logging channel. You can also redact fields in customized ways. In a Distributed Deployment, you manage each of these settings on the Edge Node, Fleet Settings, or main Settings for all Fleets.
The logging levels help to categorize the detail and severity of logged information. Choosing the right level ensures you get the information you need for troubleshooting without getting overwhelmed by a flood of data.
Here’s a breakdown of each logging level:
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
error | Logs only critical issues that have occurred, which need immediate attention to ensure the system’s integrity. |
warn | Logs warnings about potential issues that might not be critical but warrant attention to prevent future problems. |
info | Logs general information about the system’s operation, providing insights into standard processes and procedures. |
debug | Logs detailed information for diagnosing and troubleshooting potential problems, providing deep insights into the system’s behavior. |
silly | Logs extremely detailed information and metrics, primarily used for in-depth troubleshooting of inputs and other operations.Use it sparingly and only for short debugging bursts, treating it as “use at your own risk.” Enable temporarily, then disable promptly. |
Notes:
- By default, all integration logging levels are set to
info. This means logs of levelinfoand above (includingerrorandwarn) will be displayed. Manual adjustments are needed to seedebugandsillylogs. - Cribl.Cloud users cannot adjust logging levels for Worker Groups or specific integrations.
Change Logging Levels
To adjust logging levels:
From Cribl Edge’s top nav, select Settings > System > Logging > Levels.
To configure log levels on a Fleet-level, click Manage, then select the Fleet you want to configure. Next, select Fleet Settings > System > Logging > Levels.
To adjust settings on a specific Edge Node, teleport into the Node, then select Node Settings > System > Logging > Levels.
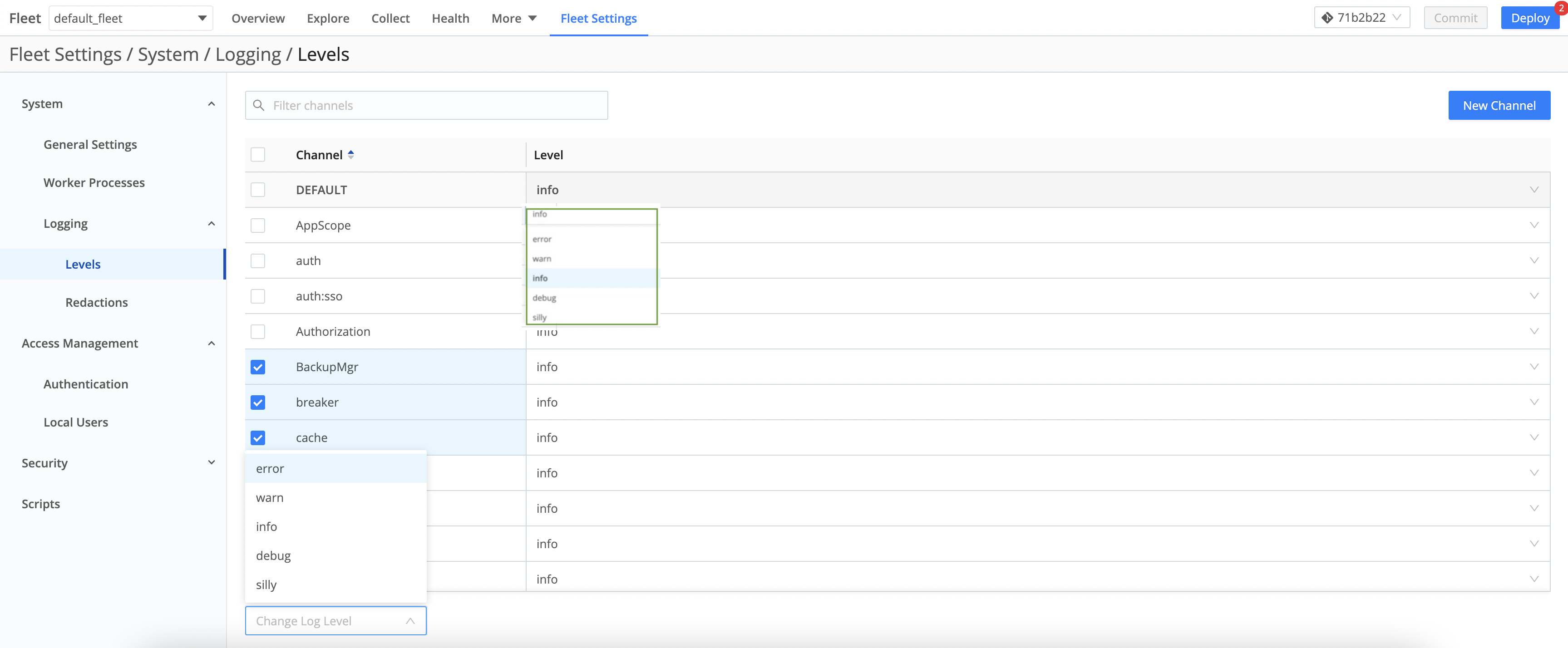
On the resulting Manage Logging Levels page, you can:
Modify one channel by clicking its Level column. In the resulting drop-down, you can set a verbosity level ranging from error up to debug. (Top of composite screenshot below.)
Modify multiple channels by selecting their check boxes, then clicking the Change log level drop-down at the bottom of the page. (Bottom of composite screenshot below.) You can select all channels at once by clicking the top check box. You can search for channels at top right.
Change Logging Redactions
On the Redact Internal Log Fields page, you can customize the redaction of sensitive, verbose, or just ugly data within Cribl Edge’s internal logs. To access these settings:
In a single-instance deployment, or for the Leader Node’s own logs, select Settings (top nav) > System > Logging > Redactions.
In a Distributed Deployment, first click Manage, then select the Fleet you want to configure. Next, select Fleet Settings > System > Logging > Redactions.
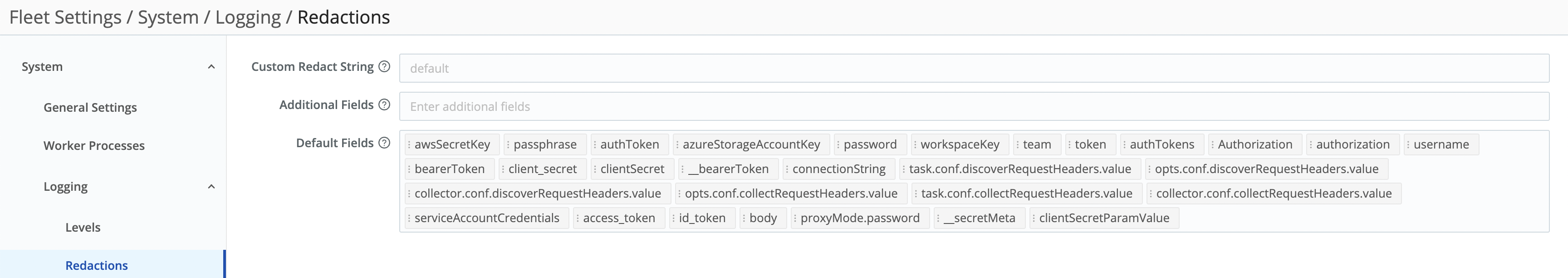
It’s easiest to understand the resulting Redact Internal Log Fields page’s fields from bottom to top:
- Default fields: Cribl Edge always redacts these fields, and you can’t modify this list to allow any of them through. However, you can use the two adjacent fields to define stricter redaction:
- Additional fields: Type or paste in the names of extra fields you want to redact. Use a tab or hard return to confirm each entry.
- Custom redact string: Unless this field is empty, it defines a literal string that will override Cribl Edge’s default redaction pattern (explained below) on the affected fields.
Default Redact String
By default, Cribl Edge transforms this page’s selected fields by applying the following redaction pattern:
- Echo the field value’s first two characters.
- Replace all intermediate characters with a literal
...ellipsis. - Echo the value’s last two characters.
Anything you enter in the Custom redact string field will override this default ??...?? pattern.





