These docs are for Cribl Edge 4.8 and are no longer actively maintained.
See the latest version (4.16).
Secure Cribl Edge Sources and Destinations with Certificates
You can use certificates and custom HTTP headers to authenticate Cribl Edge with external Sources and Destinations, enhancing the security of your data pipelines.
Setting Authentication on Sources/Destinations
You can use certificates to authenticate Cribl Edge to external data senders and receivers. You configure this at the Fleet level, as follows:
Select a Fleet.
As an alternative to the preconfiguration in steps 2-6, you can import a certificate on the fly, using the Create button for certificates in the TLS Settings for the Source or Destination.
Open Fleet Settings (top right) > Security > Certificates.
Select New Certificates.
Paste or upload
.pemfiles, as in Import Certificate and Key.Supply a Passphrase and/or CA certificate, if required by your integration partner’s certificate.
Click Save.
Open the configuration modal for the Source or Destination.
Select TLS Settings (Client Side) or TLS Settings (Server Side), depending on the integration.
Slide Enabled on.
In the Certificate name drop-down, select a certificate that you’ve preconfigured for this integration. This will auto-populate the corresponding fields here.
If you’re creating a new certificate, click the Create button beside Certificate name.
Click Save.
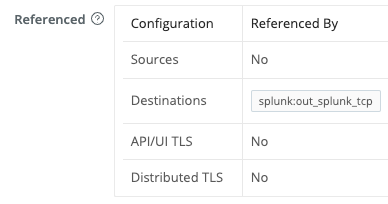
Cribl Edge will create new certificates at the same Fleet level that you’re configuring. You can verify this at the bottom of the Create new certificate modal by making sure that the Referenced table includes rows populated for the appropriate Sources and Destinations.
Custom HTTP Headers
You can also encode custom, security-related HTTP headers as needed. In a Distributed deployment, navigate to Fleet Settings, then API Server Settings > Advanced > HTTP Headers. (In a Single-instance deployment, the API Server Settings are within Global Settings > General Settings.) Define HTTP headers as key-value pairs, clicking Add Header as needed.
Implement a Custom Content Security Policy (CSP)
A Content Security Policy (CSP) helps protect Cribl Edge from Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and other web injection attacks by controlling which resources the browser is allowed to load. You can implement CSP using the Custom HTTP Headers setting described above.
Basic Configuration
To configure a basic CSP for Cribl Stream, add the following header in your HTTP Headers settings:
Header Name: Content-Security-Policy
Header Value:
default-src 'self'; script-src 'self' 'unsafe-eval' 'sha256-ZaAN8+jAf3MdnSLRdmTuExUhAwcHulq3JnLJbyqInfc=' 'sha256-+aa8QH7Wjp/9wCcmtCveJhRIN9pSaWU+Ojoe1aIvLmI='; connect-src 'self' https://cdn.cribl.io https://ai.cribl.cloud; frame-src 'self' blob: https://cdn.cribl.io; style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline'; img-src 'self' data:;Test your CSP policy thoroughly in a development environment before deploying to production and monitor the browser console for CSP violations after implementation.
SAML SSO Configuration
If your organization uses SAML Single Sign-On, you’ll need a modified CSP policy to accommodate the dynamic JavaScript and form submissions required for SAML authentication:
Header Name: Content-Security-Policy
Header Value for SAML:
default-src 'self'; script-src 'self' 'unsafe-eval' 'unsafe-inline'; connect-src 'self' https://cdn.cribl.io https://ai.cribl.cloud; frame-src 'self' blob: https://cdn.cribl.io; style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline'; img-src 'self' data:; form-action 'self' https://YOUR_IDP_DOMAIN;Replace
YOUR_IDP_DOMAINwith your actual Identity Provider’s domain (for example, your Okta domain).
SAML configurations require additional permissions that reduce the restrictiveness of the CSP compared to the basic configuration.





