Cribl Lake Destination
Send your data from Cribl Stream to Cribl Lake, using the Cribl Lake Destination.
The Cribl Lake Destination is a Cribl Stream feature that optimizes data management for two other Cribl products: It delivers data to Cribl Lake, and automatically selects a partitioning scheme that works well with Cribl Search.
Type: Non-Streaming | TLS Support: Yes | PQ Support: No
Requirements for Cribl Lake Destination
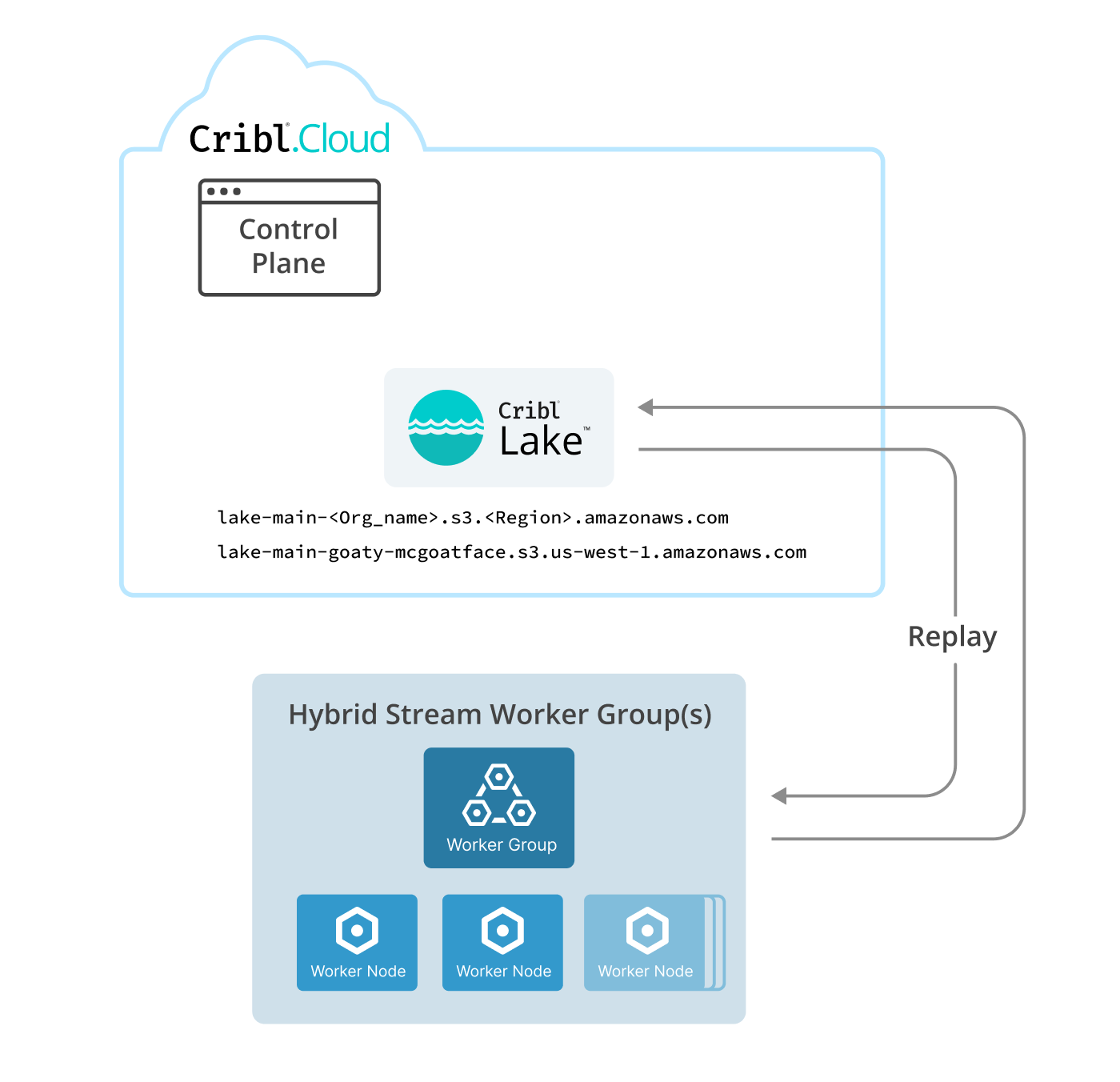
The Cribl Lake Destination can receive data from both Cribl-managed Cloud and customer-managed hybrid Stream Worker Groups. Hybrid Worker Groups must be running Cribl Stream version 4.8 or later.
On hosts for hybrid Worker Groups, this Destination requires outbound HTTP/S access to port 443. This Destination does not allow selecting a different port. For details, see Troubleshoot Hybrid Access to Cribl Lake.
Prepare Data for Use with Lakehouse
Storing data in regular Lake Datasets does not require setting a schema. However, if you want to make full use of the Lakehouse functionality, you need to make sure that events sent from Cribl Stream are parsed into distinct fields before sending to Cribl Lake/Lakehouse.
To do this, use the Stream Parser Function to ensure that all events have named fields.
Configure a Cribl Lake Destination
On the top bar, select Products, and then select Stream.
Under Worker Groups, select a Worker Group. Next, you have two options.
To configure via the graphical QuickConnect UI:
- On the Worker Groups submenu, select Routing, then QuickConnect.
- Select Add Destination at right.
- Hover over Cribl Lake from the list of tiles.
- Select Add New to open a New Destination modal.
Or, to configure via the Routing UI:
- On the Worker Groups submenu, select Data, then Destinations.
- In the Destinations tiles, select Cribl Lake.
- Select Add Destination to open a New Destination modal.
In the Destination modal, configure the following under General Settings:
- Output ID: Enter a unique name to identify this Cribl Lake Destination.
- Lake dataset: Select a Lake Dataset to send data to.
You can’t target the built-in
cribl_logsandcribl_metricsLake Datasets with this Destination.
Next, you can configure the following Optional Settings that you’ll find across many Cribl Destinations:
- Backpressure behavior: Whether to block or drop events when all receivers are exerting backpressure. (Causes might include an accumulation of too many files needing to be closed.) Defaults to
Block. - Tags: Optionally, add tags that you can use to filter and group Destinations in Cribl Stream’s Manage Destinations page. These tags aren’t added to processed events. Use a tab or hard return between (arbitrary) tag names.
- Backpressure behavior: Whether to block or drop events when all receivers are exerting backpressure. (Causes might include an accumulation of too many files needing to be closed.) Defaults to
Optionally, configure any Post-Processing settings outlined in the below sections.
Select Save, then Commit & Deploy.
Verify that data is searchable in Cribl Lake.
Processing Settings
Post-Processing
Pipeline: Pipeline or Pack to process data before sending the data out using this output.
System fields: A list of fields to automatically add to events that use this output. By default, includes cribl_pipe (identifying the Cribl Stream Pipeline that processed the event). Supports c* wildcards. Other options include:
cribl_host- Cribl Stream Node that processed the event.cribl_input- Cribl Stream Source that processed the event.cribl_output- Cribl Stream Destination that processed the event.cribl_route- Cribl Stream Route (or QuickConnect) that processed the event.cribl_wp- Cribl Stream Worker Process that processed the event.
How Cribl Stream Handles the _time Field
The Cribl Lake Destination requires _time to be a number and not null. If an incoming _time value is null or a string, this Destination will convert the value to Date.now() / 1000. This creates a time-based partitioning scheme that is readily searchable.
Troubleshooting Cribl Lake Hybrid Access
When running the Cribl Lake Destination on hybrid Worker Groups, you might receive SSL errors, or errors about being unable to connect to a host. This indicates that these Groups have restricted access to the internet through a firewall or proxy that performs SSL inspection. To reach the Cribl.Cloud Organization that hosts your Cribl Lake instance, you can remedy this as follows:
At the lower left of your Cribl.Cloud Organization, select Organization Details.
In the resulting fly-out, note the Organization ID and (AWS) Region.
Swap those two strings for the two placeholders in this fully qualified domain (FDQN) format:
lake-main-<organizationId>.s3.<region>.amazonaws.com.
With a fictional Organization ID, your FQDN might be:
lake-main-goaty-mcgoatface.s3.us-west-1.amazonaws.com.
Provide the resulting FQDN to your Security team, asking them to add a corresponding exception on the firewall or proxy.
Verify that outbound port 443 is open for HTTP/S - this is required to access the FQDN.
Test the Cribl Lake Destination: Ensure that the target URL resolves, and that Cribl Stream can successfully send data to the corresponding Lake Dataset.