Direct Access (HTTP)
Ship your data straight into Cribl Lake, bypassing Cribl Stream.
You can use the Direct Access (HTTP) option to archive data directly to Cribl Lake over HTTP from a wide variety of senders. Examples include FluentBit, Logstash, Vector, and the OpenTelemetry Collector. You will find specific configuration settings for Elasticsearch Bulk API and Splunk HEC senders.
This option bypasses routing or processing through Cribl Stream. Once your data is integrated with Cribl Lake, Cribl Stream and Cribl Search can access it as a Lake Dataset.
Create a Direct Access (HTTP) Source
You can configure one Direct Access (HTTP) Source per Workspace. (See other Limitations later in this topic.)
From the Cribl Lake sidebar, select Direct Access.
From the resulting Direct Access > New Source page, select HTTP and Next.
On the resulting Configuration page, you can select up to 10 Direct Access Datasets. (After you save this selection here, each targeted Dataset configuration will indicate HTTP Ingestion Enabled. For details, see Manage Lake Datasets.)
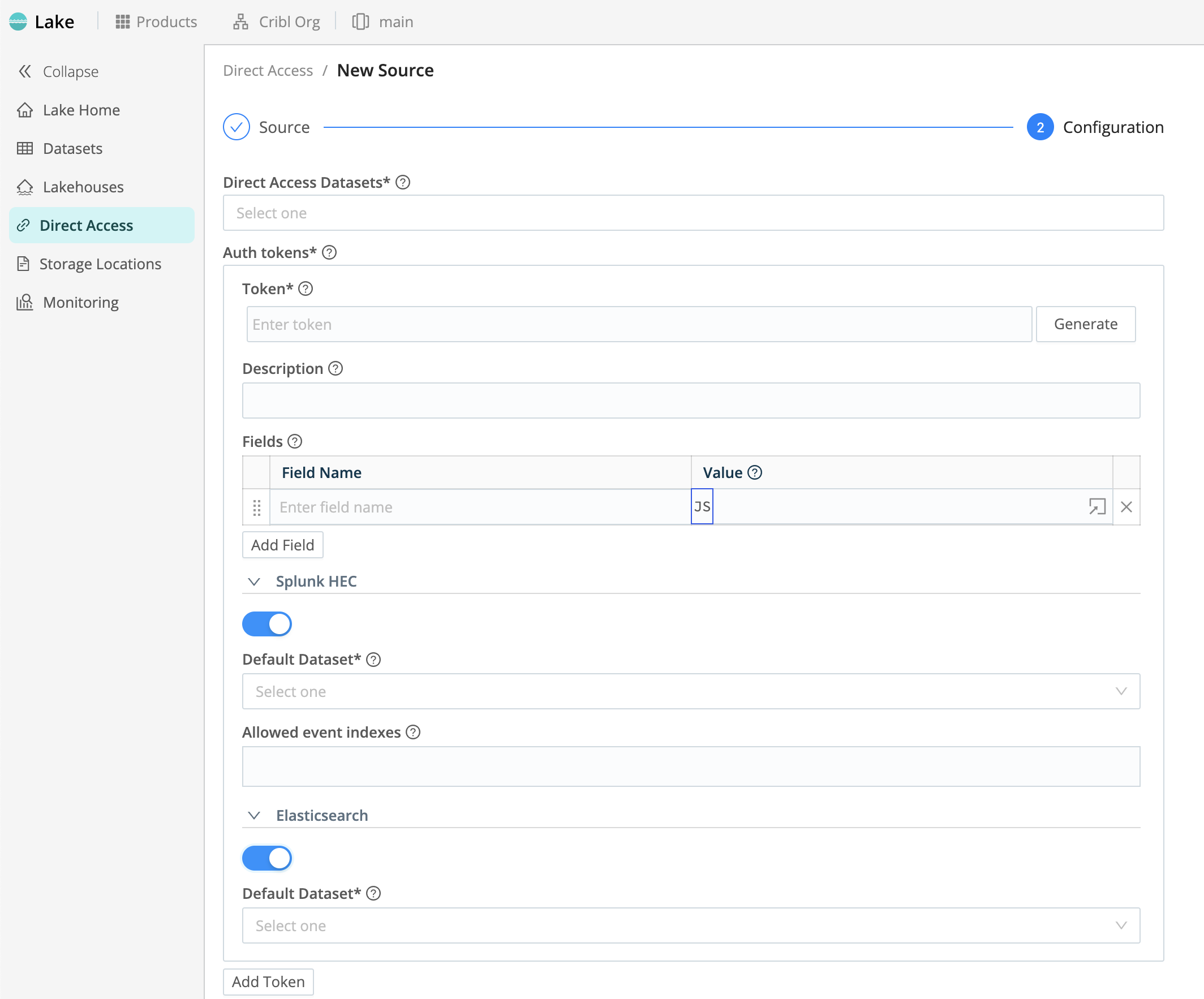
- In the Auth tokens section, you must configure at least one token, but you can add multiple tokens to authorize ingest from multiple senders. For configuration details, see Configure Auth Tokens.
Each auth token supports an optional Fields section, where you can select Add Field to tag events with key-value pairs that identify or match this token and sender. You will also see specific options for Splunk HEC and Elasticsearch Bulk API senders.
- Once you’ve configured auth tokens, select Save.
Provisioning and Ready States
For the first few minutes after you save Direct Access (HTTP) Source, you will see a badge showing that the Source is in a Provisioning state. In this state, it is setting up infrastructure and deploying onfigurations. You can’t use the Source to ingest data until it shows a Ready badge.
Once the Source moves to Ready, it is available to ingest data and store it in Lake Datasets.
Examine HTTP Ingest Endpoints
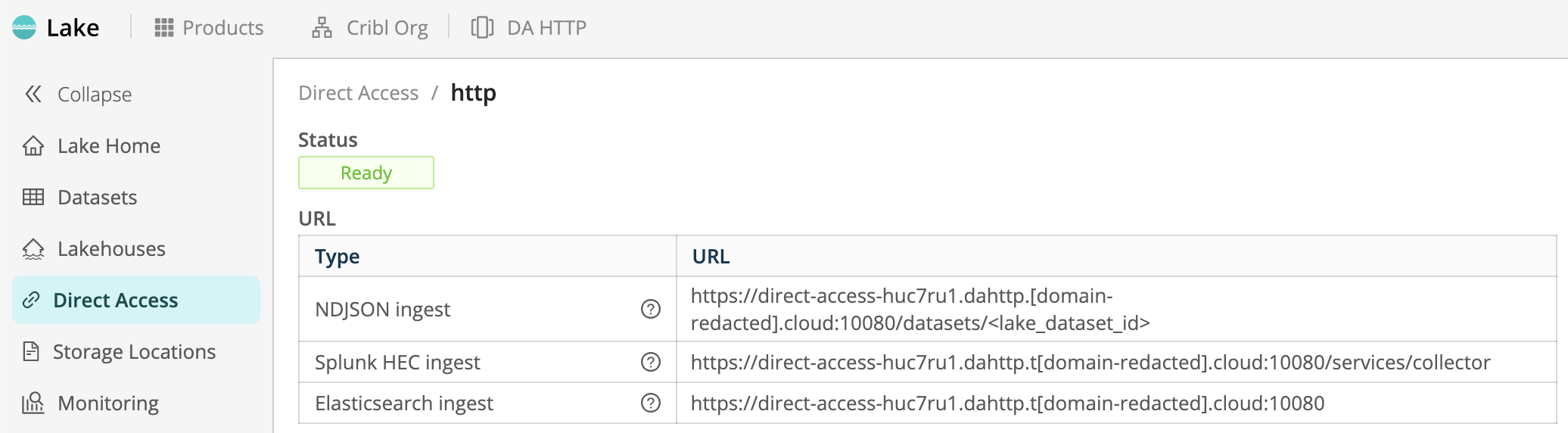
After the Source indicates Ready, select it to open its config. Here, the URL table shows you the Cribl Lake ingest endpoints that will accept data in NDJSON, Splunk HEC, and Elasticsearch Bulk API formats. As outlined in the following section, you complete each URL by replacing the <lake_dataset_id> placeholder with the ID of each target Dataset.
Send Data to Lake over HTTP
To ingest data, send a POST request to the endpoint provided in the URL of the Direct Access (HTTP) Source. Append the Lake Dataset ID to which the data should be sent. You must provide the auth token in the request header, in the format: Authorization: <my_token>. Here is an example:
curl --location "https://direct-access-huc7ru1.dev.trusting-carver-psu2edw.cribl-staging.cloud:10080/datasets/jun_26" \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Authorization: ••••••" \
--data '{"id": 974027, "name": "jnTdxFQXxd", "value": 0.1772688577715229, "timestamp": 1620759109, "extra": "0XONjJHN42BJvGz2kCAfjDUzSdIsoVhdzkrb94tVQTgXdlbXXP"}'Send Data to Lake with Vector
Vector is one agent that is compatible with Direct Access. To send data to a Cribl Lake Dataset with Vector:
- In Cribl Lake, from your Direct Access (HTTP) Source page: Copy the Ingest URL, appending the ID of your target Dataset.
- In Vector, configure an HTTP sink to the resulting endpoint.
- As shown in the sample YAML below, your request headers must provide the auth token, in the format:
Authorization: <token>.
cribl_lake_http:
type: http
inputs: ["<vector_sink_or_transform"]
request:
headers:
authorization: "<token>"
encoding:
codec: "json"
json:
pretty: true
uri: https://direct-access-huc7ru1.<tenant_id>.cribl.cloud:10080/datasets/<dataset_id>Configure Auth Tokens
Here, you define the authentication token required to access each corresponding sender’s inbound data. Ensure that the token is valid and has the necessary permissions for data retrieval. Select Add Token to define more tokens. For each token, you can configure the following settings, with specific options available for Splunk HEC and Elasticsearch senders.
Token: Enter your token here. You also have the option to Generate a new token.
Description: Optionally, enter a summary of this token’s purpose. Recommended, because the description becomes a friendly display name for each token.
Fields: Fields to add to events referencing this token. Each field is a Name/Value pair.
Fields that you specify here will normally override fields of the same name in events. However, you can specify that event fields’ values should prevail.
In particular, where inbound events have no
indexfield, this Source adds one with the literal valuedefault. You can override this value by using Add Field to specify anindexfield, and then setting its Value to an expression of the following form:index == 'default' ? 'myIndex' : index
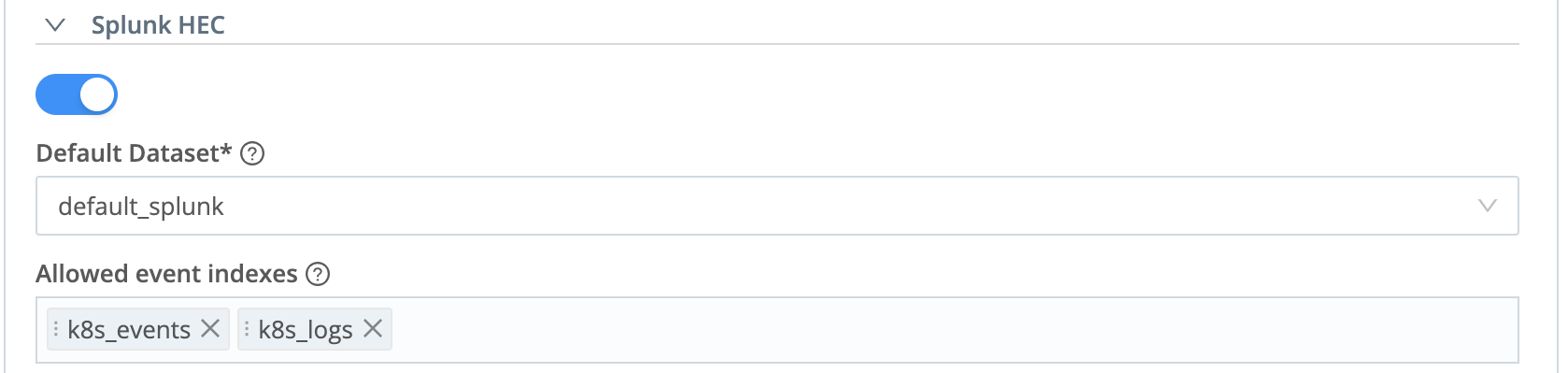
Splunk HEC Token Options
The Direct Access (HTTP) Source will inspect each Splunk HEC event, looking for a field named index that is sent by a Splunk Heavy Forwarder. Ideally,the index field’s value should match an identically named Cribl Lake Dataset.
If Direct Access finds no index, or if the index value does not match a Cribl Lake Dataset, it will store the data in the Dataset that you select in the Default Dataset drop-down.
Allowed Event Indexes
In this optional field, you can specify which Splunk HEC event indexes are permissible for events ingested using this token. (Cribl Lake will reject requests whose indexes don’t match strings or patterns here.) Leave empty to accept all events. You can enter multiple index values, and you can use wildcards (*) for pattern matching.
Events lacking any
indexfield will still be ingested into thehec_syslog_dafallback Dataset.
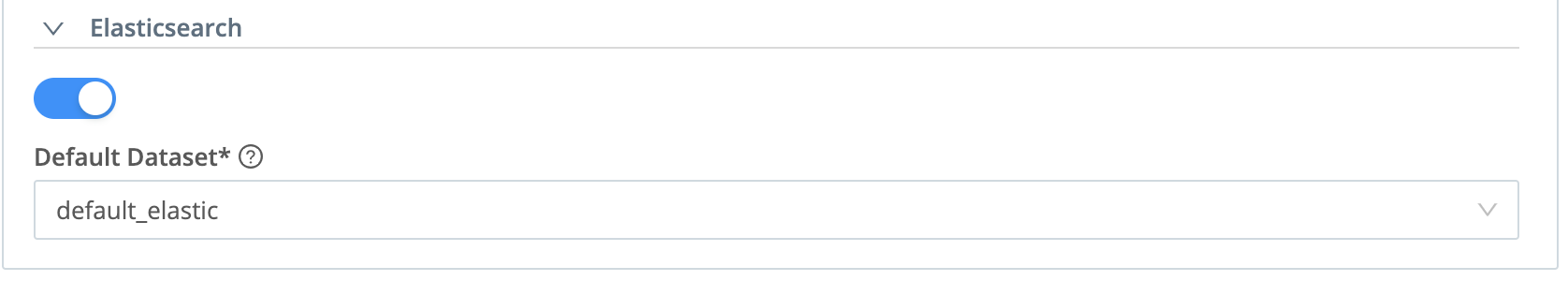
Elasticsearch Token Options
For data sent via the ElasticSearch Bulk API, the Direct Access (HTTP) Source will inspect each event, looking for a field named index that is sent by a compatible agent. Ideally,the index field’s value should match an identically named Cribl Lake Dataset.
If Direct Access finds no index, or if the index value does not match a Cribl Lake Dataset, it will store the data in the Dataset that you select in the Default Dataset drop-down.
Token Monitoring
To filter on token values in Lake Monitoring, use __hecToken for all senders - not just Splunk HEC - rather than using the simpler __token.
Limitations of Direct Access (HTTP)
As noted above, you can configure one Direct Access (HTTP) Source per Workspace. This Source can manage up to 10 Datasets.
A Lake Dataset populated via Direct Access must use the default Cribl Lake Storage Location, not an external bucket.





