Cribl.Cloud Identity and Authorization Model
This document explains the foundational security model for Cribl.Cloud, covering identity, authentication, and authorization for Users, Organizations, and Workspaces.
SSO and Enterprise Integration
For federated authentication, Cribl.Cloud offers Single Sign-On (SSO) integration with existing enterprise identity systems. We support industry-standard protocols, including Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) and OpenID Connect (OIDC). This allows you to centralize user management in your existing identity provider (IdP), such as Active Directory, Okta, or Ping Identity, and enable seamless, secure access to your Cribl.Cloud Organization.
For details, see (SSO on Cribl.Cloud)[/stream/sso-cloud].
Cribl.Cloud Identity and Access Model
The relationships between Users, Organizations, and Workspaces can be understood as a sequential process that defines a member’s access.
The following a high-level overview of the Cribl.Cloud logical model, illustrating the relationships between a user, the shared multi-tenant services, and the single-tenant organization with its Workspaces.
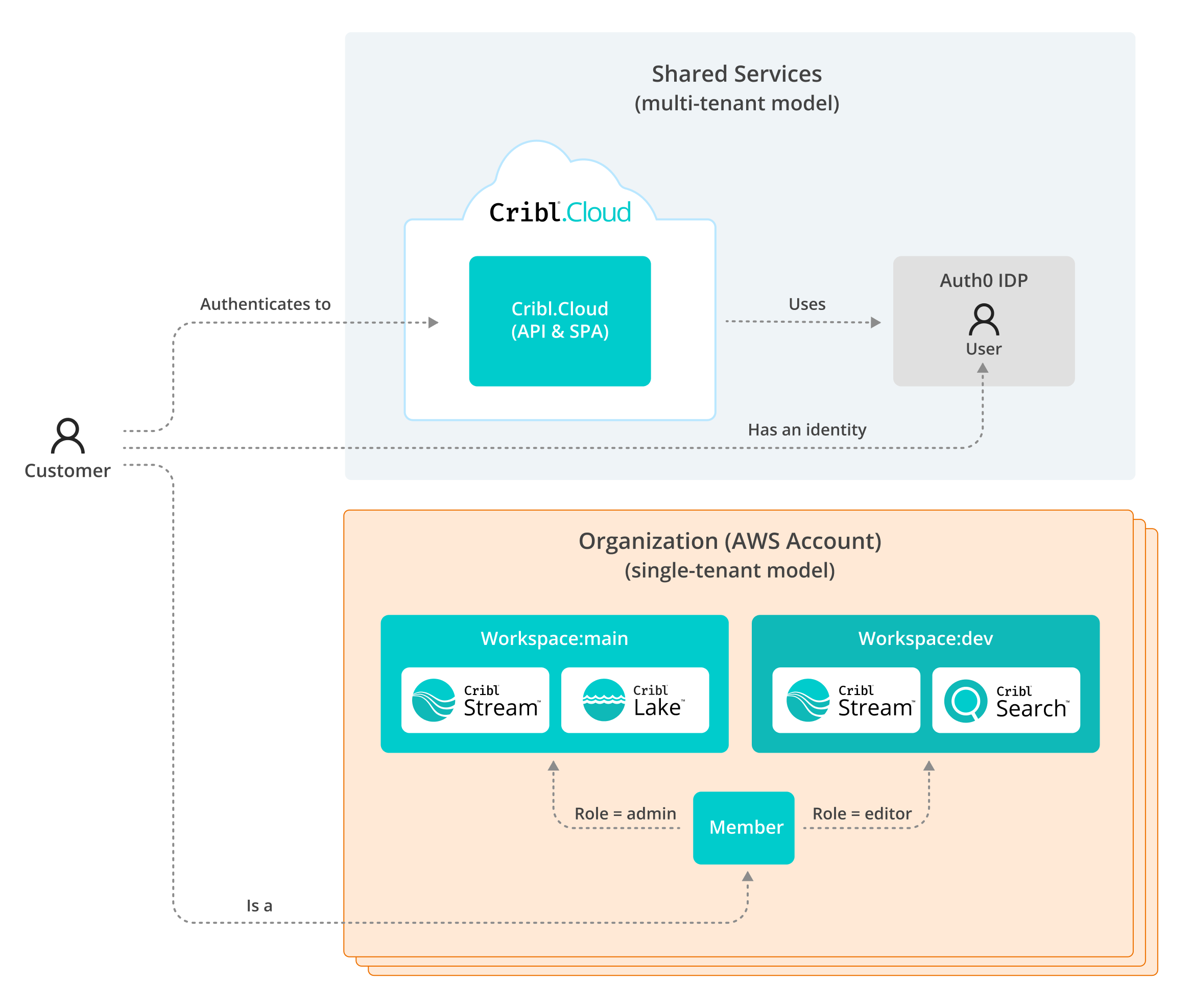
User Authentication Flow
When a user logs in via SSO, the process follows a standard Service Provider-initiated flow.
- A Cribl.Cloud User attempts to access their Organization.
- Cribl.Cloud, acting as the Service Provider (SP), redirects the user’s browser to your configured Identity Provider (IdP).
- The IdP prompts the user for credentials and authenticates them.
- Upon successful authentication, the IdP sends a signed response (SAML assertion or OIDC token) back to the user’s browser.
- The browser forwards this response to Cribl.Cloud.
Cribl.Cloud verifies the signed response, validates the user’s identity, and grants access based on their assigned roles.
User Provisioning and Access Model
With SSO, user provisioning is handled automatically. When a user logs in for the first time via your Identity Provider (IdP), Cribl.Cloud receives and ingests core attributes–like email, first name, last name, and group memberships–to automatically provision their account. This eliminates the need for you to manually create accounts. For details, see (SSO on Cribl.Cloud)[sso-cloud].
Once provisioned, the user becomes a Member of a single Organization, which is a logical container for your Cribl products. You can have multiple Workspaces within your Organization. A user’s permissions and roles are dynamically managed by their group membership in your IdP, which grants access to specific Workspaces and resources.
For details, see Members and Permissions.
Authorization and Access Control
In Cribl.Cloud, Authentication (AuthN) is the process of verifying who you are, while Authorization (AuthZ) determines what you can do.
The platform uses two separate authorization systems to manage access:
- Separate authorization mechanism for the Organization Management Portal and its APIs, handling permissions for tasks like creating Workspaces and managing members.
- The Control Plane (Leader) implements its own authorization system for all workspace-level features and in-product access controls.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and IdP Group Mapping
Our access control methods are primarily Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), where roles grant access based on a defined set of permissions. There are two types of roles:
- System Roles are administrative roles for internal use only and are not granted to customers (for example,
cloud_admingrantsread/writeaccess to all Organization APIs). - Organization Member Roles are assigned to customers within a specific Organization and define what they can do. Examples include
org_owner,org_admin, and more granular roles for Workspaces and products likews_ownerorproduct_reader.
You can map user groups from your IdP to specific Cribl roles. This is a critical feature that allows you to manage all user access and permissions centrally within your existing IdP, rather than creating and managing separate local accounts.
Roles are managed via User Groups in the IdP, and the Role name follows the convention: cribl:<organization_name>:MyCompany_CriblAdmins to the cribl:my-org:admin Role in Cribl. This mapping automatically grants the appropriate permissions to Users in that Group.
For details, see External Groups and Cribl Stream Roles.
Fine-Grained Permissions
These roles are mapped to Fine-Grained Permissions that grant access to specific API resources. For example, the can_read_connections permission allows a Role to access the /organizations/{organizationId}/connections/sso API endpoint with a GET method.
API Credentials (Client Credentials)
For machine-to-machine applications, access to the Leader APIs is granted through API Credentials (Client Credentials). This allows you to programmatically perform actions without a real user login. The authorization system establishes relationships for these credentials, checking their permissions just like it does for human users.
For details, see Cribl API.





