Connect Cribl Search to Data Lake Amazon S3
Configure Cribl Search to query Cribl Stream’s Data Lake Amazon S3 Destination.
Cribl Stream’s Data Lake Amazon S3 Destination sends data to Amazon S3 with a partitioning scheme tailored for Cribl Search. This scheme optimizes how objects are searched relative to the search’s time range.
In this guide, you’ll set up a Dataset Provider and a Dataset to search objects that Cribl Stream has exported to your Amazon S3 bucket via a Data Lake Amazon S3 Destination.
Data transfer costs and other charges might apply. For details, see the Data Transfer Charges section below.
Add a Data Lake Amazon S3 Dataset Provider
A Dataset Provider tells Cribl Search where to query, and contains access credentials. Here, you will add an Amazon S3 Dataset Provider.
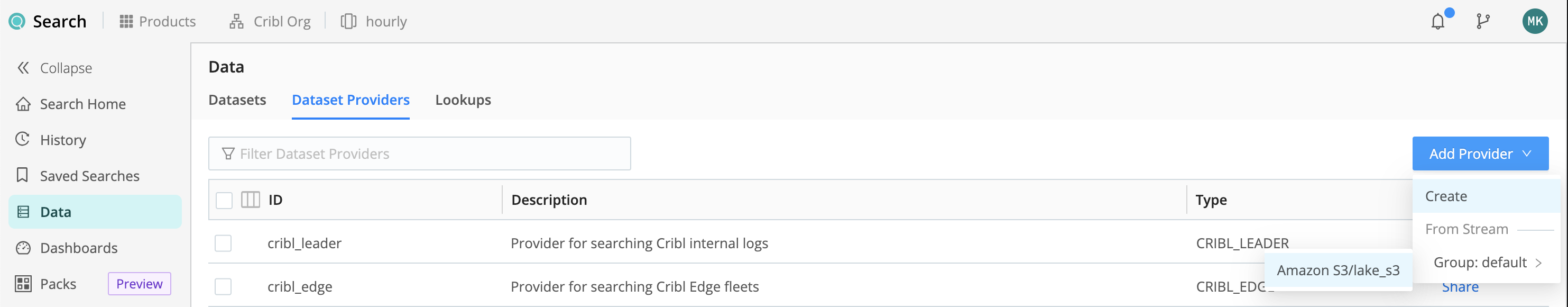
To add a new Dataset Provider, select Data, then Dataset Providers, then Add Provider.
From the resulting drop-down, select the Cribl Stream Worker Group and the Data Lake Amazon S3 Destination you want to search.
Basic Configuration
Configure the resulting New Dataset Provider modal as follows:
- ID is a unique identifier for the Dataset Provider. This is how you’ll reference it when assigning Datasets to
it. Start the ID with a letter; the rest of the ID can use letters, numbers, and underscores (for example,
my_dataset_provider_1). - Description is optional. Here, you can enter a summary that will clarify this Dataset Provider’s purpose to other users.
- Set the Dataset Provider type to
Amazon S3. - Authentication method is automatically populated with the credentials used by the Data Lake Amazon S3 Destination. You can use different credentials if desired - you have two options, Assume Role and AWS keys. For details on configuring each option, see Authentication Method below.
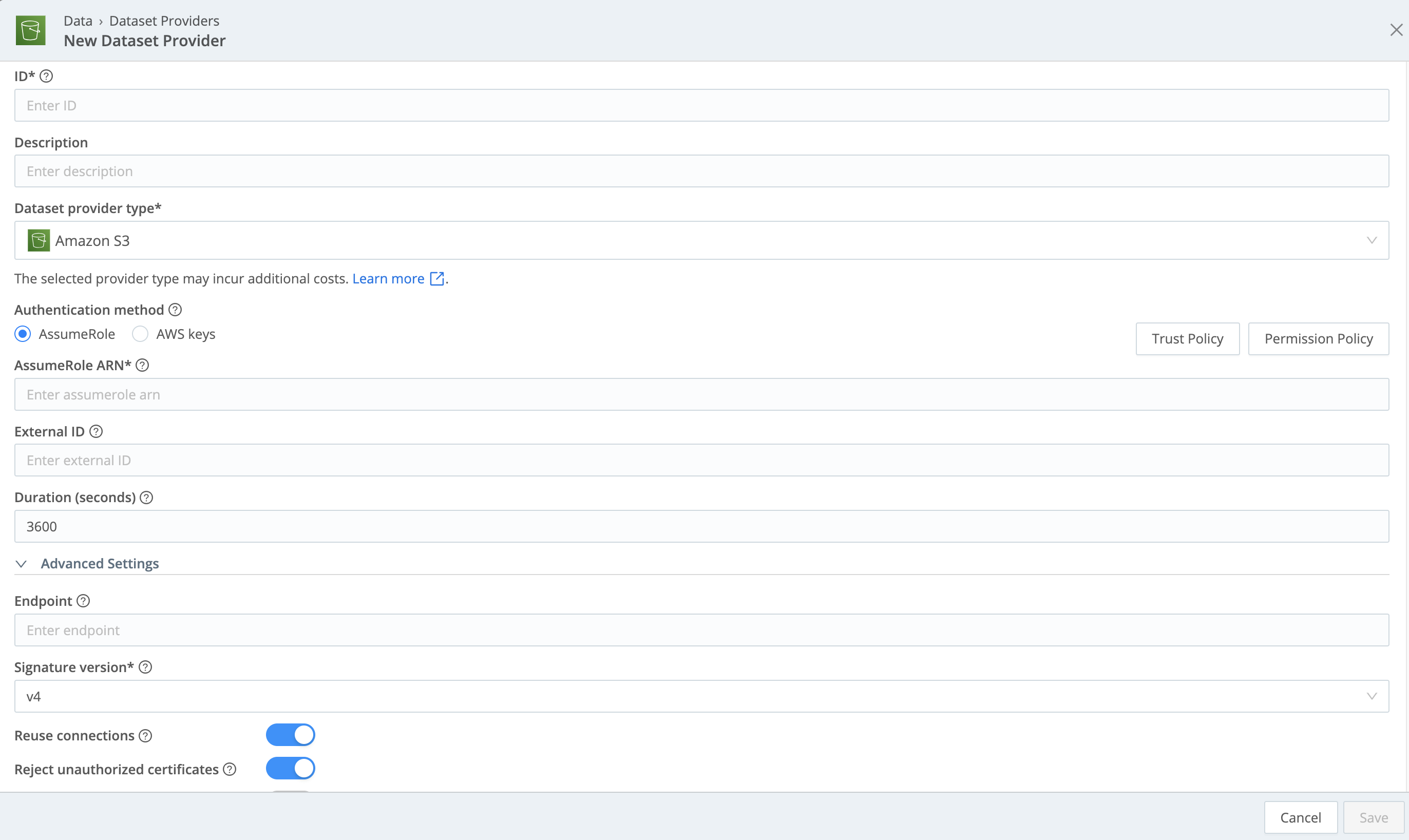
Advanced Settings
This section provides the following optional configurations:
- Endpoint: S3 service or compatible endpoint. If empty, defaults to AWS Region-specific endpoint.
- Signature version: Signature version to use for signing S3 requests. Defaults to
v4. - Reuse connections: Whether to reuse connections between requests. Toggling on (default) can improve performance.
- Reject unauthorized certificates: Whether to reject certificates that cannot be verified against a valid Certificate Authority (for example, self-signed certificates). Defaults to toggled on.
Wrapping Up
Select Save when your configuration is complete.
Authentication Method
Your choices here are AssumeRole or AWS keys. For rich details on both options, beyond the configuration basics in this section, see Grant Access to AWS.
AssumeRole Authentication
Selecting AssumeRole requires the IAM role’s ARN (AssumeRole ARN), and also exposes the following options:
The External ID on this Dataset Provider must match the external ID defined in the IAM Role Trust Policy.
The Duration (seconds) defines how long the AssumeRole’s session lasts. Minimum is
900(15 minutes), default is3600(1 hour), and maximum is43200(12 hours).The ABAC tagging controls described in the next section.
To the right, select the Trust Policy and Permission Policy buttons to see the default policies that you can copy and expand, so you don’t have to write them from scratch. For more information, see Example Trust Policy and Expand the Permission Policy.
AWS Keys Authentication
Selecting AWS keys requires the IAM user’s Access key and Secret key.
To the right, select the Permission Policy button to see the default policy that you can copy and expand, so you don’t have to write it from scratch. For more information, see Expand the Permission Policy.
Permissions for Data Lake Amazon S3
The following permissions are needed to read from an Amazon S3 bucket:
s3:GetObjects3:ListBucket
If you’re using the same IAM policy for this Dataset as the Data Lake Amazon S3 Destination, you need to provide permissions to read and write:
s3:GetObjects3:ListBuckets3:GetBucketLocations3:PutObject
Add a Data Lake Amazon S3 Dataset
Now you’ll add a Dataset that tells Cribl Search what data to search from the Dataset Provider.
To add a new Dataset, select Data, then Datasets, then Add Dataset.
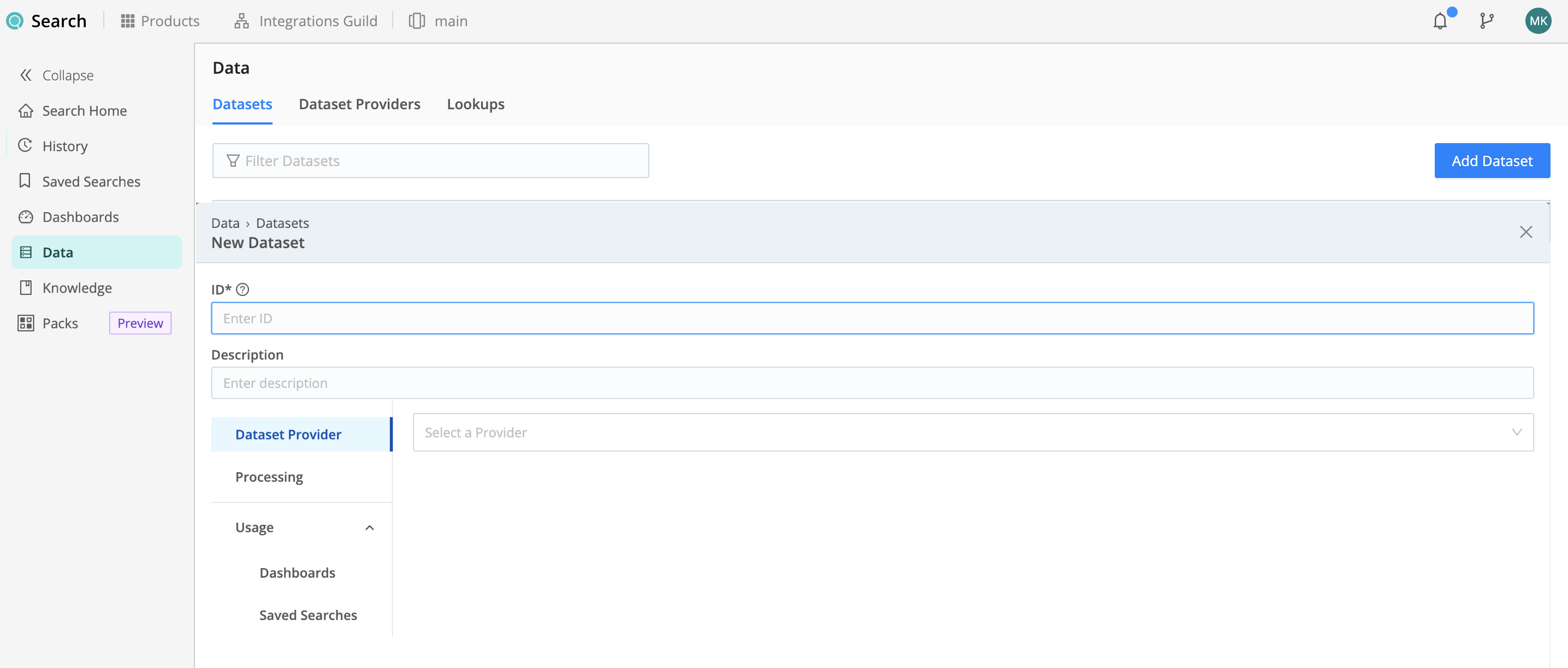
Configure the New Dataset modal as follows.
Identify the Dataset
- ID is an identifier unique both in Cribl Search and in your Amazon S3 data lake. You’ll use this to specify the
Dataset in a query’s scope, telling Cribl Search to search the Dataset. Start the ID with a letter; the rest of the ID can use letters, numbers, and underscores (for example,
my_dataset_1). - Description is optional. Here, you can enter a summary that will clarify this Dataset’s purpose to other users.
- Set Dataset Provider to the Amazon S3 Dataset Provider (its ID) that you created in the above Add a Data Lake Amazon S3 Dataset Provider section.
Set Up Path and Region
Configure the path and Region as follows:
- Bucket path is the path to the S3 objects you’d like to search. Through Cribl Stream’s Data Lake Amazon S3 Destination, data is partitioned specifically for Cribl Search and sent to Amazon S3. A time-based search scheme optimizes how objects are searched.
The Bucket path is automatically populated to use this scheme, starting with the bucket name followed by time tokens:
<my-bucket-name>/${*}-${_time:%Y}/${*}-${_time:%m}/${*}-${_time:%d}/${*}-${_time:%H}.
Tokens and key-value pairs are supported, see bucket path for details.
Path filter is a JavaScript filter expression that is evaluated against the S3 bucket path. Defaults to
true, which matches all data, but you can customize this value.Toggle off Auto-detect region if you want to use the adjacent Region drop-down to specify the AWS Region where the S3 bucket is located. When toggled on, Cribl automatically detects the Region and locks the drop-down.
The Amazon S3 Dataset type supports multiple path/filter/region configurations per bucket. For details about this option, see Multiple Path Configs.
Set Up Datatypes and Storage Classes
On the Processing left tab, you specify Datatypes to break data down into discrete events and define fields so they’re ready to search.
Use the drop-down to set the first rule to AWS Datatypes. Optionally, click Add Datatype Ruleset to select more
rulesets - each of which contains rules applied to the data searched in your Dataset. For details, see
Datatypes.
On the Storage classes left tab, select the storage classes that you want this Dataset to search against. You can minimize retrieval costs by selecting only warmer classes. You must select at least one class. For details, see Storage Classes.
Save the Configuration
Bypass the Usage left tabs for now, and select Save when your configuration is complete.
Path/Filter Considerations
This section offers details and guidance on configuring search paths and filters.
Bucket Path
The Bucket path specifies the data that the Dataset consists of. It defines the scope of data, to narrow down what data is in the Dataset. This is a JavaScript expression that supports tokens and key-value pairs. For example,
my-bucket/${data}/- wheredatabecomes a field for all events of that Dataset.my-bucket/${data}/${*}- wheredataand the wildcarded path becomes a field for all events of that Dataset.
To search partitioned data in S3, the bucket path includes the partition keys and their corresponding values using URL
encoding, where %3D replaces =. For example, the bucket path for data in env and service partitions is
my-bucket/env%3D${env}/service%3D${service}/.
Basic Tokens
Basic tokens’ syntax follows that of JS template literals: ${token_name} - where token_name is the field (name) of interest.
For example, if the path was set to /var/log/${hostname}/${dataSource}/, you could use a filter such as hostname=='myHost' && dataSource=='mydataSource' to specify data only from the /var/log/myHost/mydataSource/ subdirectory.
Time-Based Tokens
Paths with time notation can be referenced with tokens, having a direct effect on the earliest and latest boundaries. The supported time fields are:
_timeis the raw event’s timestamp.__earliestis the search start time.__latestis the search end time.
Time-based tokens are processed as follows:
- For each path, times must be notated in descending order. So Year/Month/Day order is supported, but Day/Month/Year is not.
- Paths may contain more than one time component. For example,
/my/path/2020-04/20/. - In a given path, each time component can be used only once. So
/my/path/${_time:%Y}/${_time:%m}/${_time:%d}/...is a valid expression format, but/my/path/${_time:%Y}/${_time:%m}/${host}/${_time:%Y}/...(with a repeatedY) is not supported. - For each path, all extracted dates/times are considered in UTC.
Cribl recommends that your path always include and tokenize the largest available time fields, proceeding down to the smallest desired time fields. Otherwise, your searches might yield unexpected results, because Cribl Search will default the omitted fields to their earliest allowed value.
The following strptime format components are allowed:
Y,yfor yearsm,B,b,efor monthsd,jfor daysH,Ifor hoursMfor minutesSfor secondssfor Unix time (seconds since 1/1/1970)
Time-based token syntax follows that of a slightly modified JS template literal:
${_time: some_strptime_format_component}. Examples:
| Path | Matches |
|---|---|
/path/${_time:%Y}/${_time:%m}/${_time:%d}/... | /path/2020/04/20/... |
/path/${_time:year=%Y}/${_time:month=%m}/${_time:day=%d}/... | /path/year=2020/month=05/day=20/... |
/path/${_time:%Y-%m-%d}/... | /path/2020-05-20/... |
Path Filter
This is a JavaScript filter expression that Cribl Search evaluates against the corresponding Bucket path.
The Path filter field’s value defaults to true, which matches all data. However, you can customize this value
almost arbitrarily.
For example, with this Path filter:source.endsWith('.log') || source.endsWith('.txt')
…this configuration will search only files/objects with .log or .txt extensions.
At the Path filter ffield’s right edge are a Copy button and an Expand button that opens a validation modal.
Search Data Lake Amazon S3
Now that you have a Dataset Provider and Dataset, you’re ready to start searching.
Data Transfer Charges
Data transfer to Cribl Search is free if your S3 bucket is in the same Region as your Cribl.Cloud Workspace.
Data transfer to Cribl Search is subject to AWS data transfer costs if your S3 bucket is not in the Regions supported by Cribl.Cloud. See the Data transfer section in Amazon S3 Pricing.
Cribl Search will try to minimize the amount of data transferred, to the extend possible, by using path filters, pruning, and other methods.
Other Charges
Other charges may apply. For example, LIST and GET requests to your S3 buckets will be charged per AWS S3. See the Requests & data retrievals section in Amazon S3 Pricing.





