These docs are for Cribl Stream 4.4 and are no longer actively maintained.
See the latest version (4.16).
Bootstrap Workers from Leader
Boot fully provisioned Workers
Cribl Stream Workers can completely provision themselves, directly from the Leader, upon initial boot. This means that a group of any number of Workers can launch and be fully functional within the cluster, in seconds.
How Does It Work?
A Cribl Stream Leader Node provides a bootstrap API endpoint, at /init/install-worker.sh, which returns a shell script. You can run this shell script on any supported machine (see Restrictions below), without Cribl Stream installed. This fully provisions the machine as a Worker Node.
Although you can specify the download URL when you execute the initial curl command, the Cribl Stream package is not downloaded until you generate the script via the API, and then execute it.
For additional information on using environment variables to set the hostname, see Setting the Hostname.
Requirements
All Worker Nodes’ hosts must enable ongoing outbound communication to the Leader’s port 4200, to enable the Leader to manage the Workers. While the bootstrap script runs, firewalls on each Worker’s host must also allow outbound communication on the following ports:
- Port 443 to
https://cdn.cribl.io. - Port 443 to a Cribl.Cloud Leader.
- Port 9000 to an on-prem Leader.
If any of this traffic must go through a proxy, see System Proxy Configuration for configuration details. To anticipate and resolve edge cases not mentioned here, see Restrictions below.
Troubleshooting Root Access or SSL Errors
The script will install Cribl Stream into
/opt/cribl, and will make system-level changes. For systems like Ubuntu, which don’t allow direct root access, you’ll need to use thesudoprefix when executing the script.The script will create a user named
criblto install, own, and run Cribl Stream/Edge.If you encounter errors of this form:
ssl certificate problem: self signed certificate in certificate chain
…add the-kflag to disable certificate validation.
UI Access
Cribl Stream admins can use the UI to concatenate and copy/paste the bootstrap script, automating several steps below. You can use an adjacent option to grab a script that updates a Worker’s Group assignment.
To use these options, you must have the
adminRole on a distributed deployment’s Leader Node, with an Enterprise license. You must also create the Worker Groups before using the following instructions to add or reassign Workers to them.
Add/Bootstrap New Worker
From Cribl Stream’s top nav, select Manage > Groups.
Click the link in your desired Group’s Workers column.
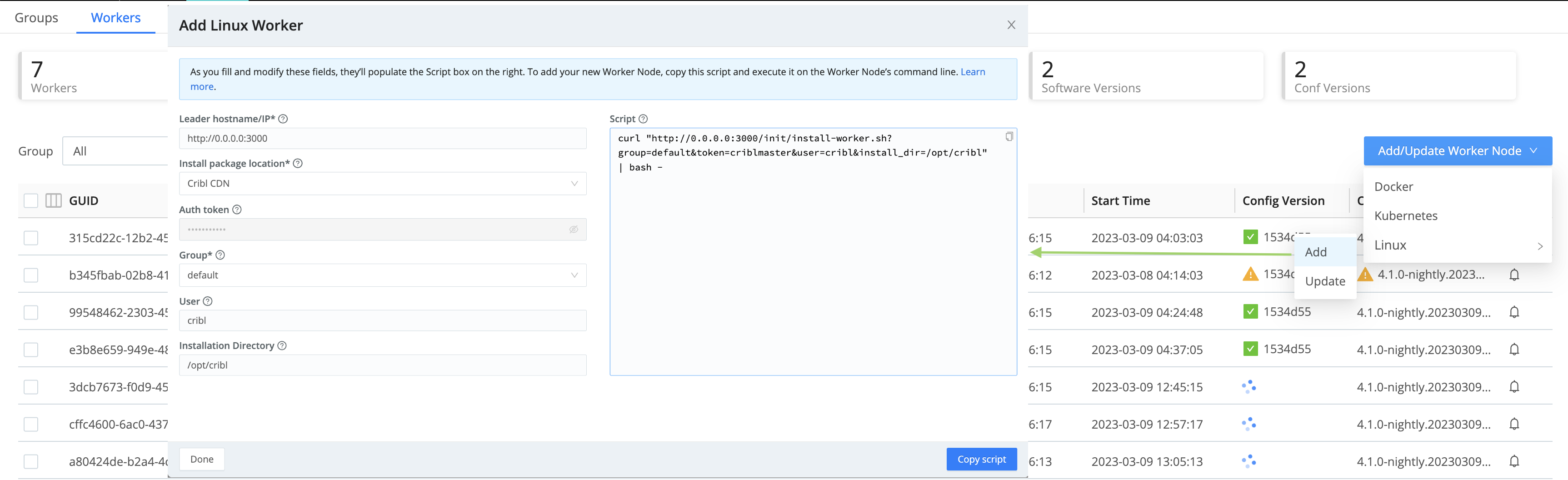
On the resulting Workers tab, click Add/Update Worker at the upper right.
Select Bootstrap new from the menu, as shown in the composite screenshot below.
In the resulting Add Worker modal, the Cribl Stream package location defaults to
Cribl CDN. If desired, change this toDownload URL. (For details about this option, see Adding Download URL.)As needed, correct the target Group, as well as the Leader hostname/IP (URI).
Copy the resulting script to your clipboard.
Click either OK or Cancel to close the modal.
Paste the script onto your Worker Node’s command line and execute it, to add the Worker.
- As needed (see the note above), prepend
sudoto the generated Script field’s contents, and/or append the-kflag.
- As needed (see the note above), prepend
Update Existing Worker
You can also auto-generate a script that will update an existing Worker’s Group assignment, and/or assign the Worker to a different Leader:
Follow steps 1-2 in Add/Bootstrap New Worker above.
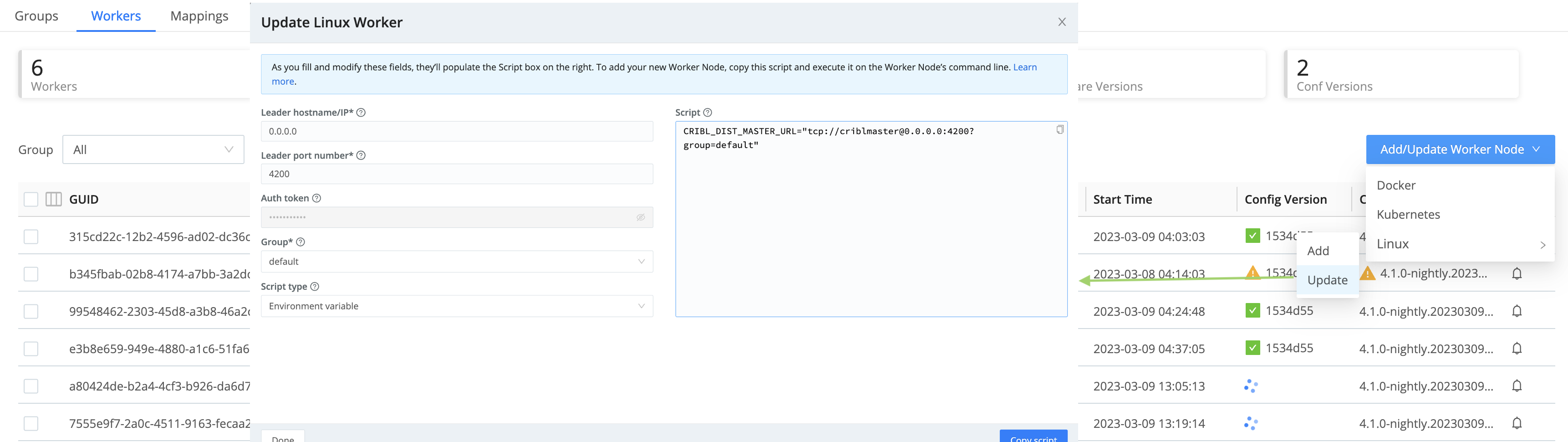
From the Add/Update Worker menu, select Update existing.
In the resulting Update Worker modal, select the new target Group for this Worker.
As needed, correct or change the Leader hostname/IP and/or Leader port number.
The Script type drop-down defaults to the
Environment variableoption for generating the script’s command. If you’re not relying on environment variables, change this toCLI.Copy the resulting script to your clipboard.
Click either OK or Cancel to close the modal.
Paste the script onto your Worker Node’s command line and execute it, to update the Worker’s assignment.
- As needed (see the note above), prepend
sudoto the generated Script field’s contents, and/or append the-kflag.
- As needed (see the note above), prepend
API Spec
Request Format
GET http://<leader hostname or IP>:9000/init/install-worker.sh
Query Strings
| String | Required? | Description |
|---|---|---|
token | optional | Leader Node’s shared secret (authToken). By default, this is set to criblmaster. You can find this secret in the Leader Node’s Distributed Settings section. |
group | optional | Name of the cluster’s Worker Group. If not specified, falls back to default. |
download_url | optional | Provide the complete URL to a Cribl Stream installation binary. This is especially useful if the Worker Nodes don’t have access to the Internet to download from cribl.io. |
tag | optional | When used in conjunction with Mapping Rules, enables you to specify the Worker Group you want the bootstrapped Worker to join. Multiple tags should be in the form &tag=tag1&tag=tag2. |
Example HTTP Request
GET http://<leader hostname or IP>:9000/init/install-worker.sh?token=79364d6e-dead-beef-4c6e-554445664867As of version 3.0, Cribl Stream’s former “master” application components are renamed “leader.” While some legacy terminology remains within CLI commands/options, configuration keys/values, and environment variables, this document will reflect that.
Example Response
#!/bin/sh
### START CRIBL LEADER TEMPLATE SETTINGS ###
CRIBL_MASTER_HOST="<Master FQDN/IP>"
CRIBL_AUTH_TOKEN="<Auth token string>"
CRIBL_VERSION="<Version>"
CRIBL_GROUP="<Default group preference>"
CRIBL_MASTER_PORT="<Master heartbeat port>"
CRIBL_DOWNLOAD_URL="<download url>"
### END CRIBL MASTER TEMPLATE SETTINGS ###
# Set defaults
checkrun() { $1 --help >/dev/null 2>/dev/null; }
faildep() { [ $? -eq 127 ] && echo "$1 not found" && exit 1; }
[ -z "${CRIBL_MASTER_HOST}" ] && echo "CRIBL_MASTER_HOST not set" && exit 1
CRIBL_INSTALL_DIR="${CRIBL_INSTALL_DIR:-/opt/cribl}"
CRIBL_MASTER_PORT="${CRIBL_MASTER_PORT:-4200}"
CRIBL_AUTH_TOKEN="${CRIBL_AUTH_TOKEN:-criblmaster}"
CRIBL_GROUP="${CRIBL_GROUP:-default}"
if [ -z "${CRIBL_DOWNLOAD_URL}" ]; then
FILE="cribl-${CRIBL_VERSION}-linux-x64.tgz"
CRIBL_DOWNLOAD_URL="https://cdn.cribl.io/dl/$(echo ${CRIBL_VERSION} | cut -d '-' -f 1)/${FILE}"
fi
UBUNTU=0
CENTOS=0
AMAZON=0
echo "Checking dependencies"
checkrun curl && faildep curl
checkrun adduser && faildep adduser
checkrun usermod && faildep usermod
BOOTSTART=1
SYSTEMCTL=1
checkrun systemctl && [ $? -eq 127 ] && BOOTSTART=0
checkrun update-rc.d && [ $? -eq 127 ] && BOOTSTART=0
echo "Checking OS version"
lsb_release -d 2>/dev/null | grep -i ubuntu && [ $? -eq 0 ] && UBUNTU=1
cat /etc/system-release 2>/dev/null | grep -i amazon && [ $? -eq 0 ] && AMAZON=1
echo "Creating cribl user"
if [ $UBUNTU -eq 1 ]; then
adduser cribl --home /home/cribl --gecos "Cribl Stream User" --disabled-password
fi
if [ $CENTOS -eq 1 ] || [ $AMAZON -eq 1 ]; then
adduser cribl -d /home/cribl -c "Cribl Stream User" -m
usermod -aG wheel cribl
fi
echo "Installing Cribl Stream"
mkdir -p ${CRIBL_INSTALL_DIR}
curl -Lso ./cribl.tar.gz "${CRIBL_DOWNLOAD_URL}"
tar xzf ./cribl.tar.gz -C ${CRIBL_INSTALL_DIR} --strip-components=1
rm -f ./cribl.tar.gz
chown -R cribl:cribl ${CRIBL_INSTALL_DIR}
if [ $BOOTSTART -eq 1 ]; then
echo "Setting Cribl Stream to start on boot"
${CRIBL_INSTALL_DIR}/bin/cribl boot-start enable -u cribl
fi
mkdir -p ${CRIBL_INSTALL_DIR}/local/_system
cat <<-EOF > ${CRIBL_INSTALL_DIR}/local/_system/instance.yml
distributed:
mode: worker
master:
host: ${CRIBL_MASTER_HOST}
port: ${CRIBL_MASTER_PORT}
authToken: ${CRIBL_AUTH_TOKEN}
tls:
disabled: true
group: ${CRIBL_GROUP}
EOF
chown -R cribl:cribl ${CRIBL_INSTALL_DIR}
if [ $BOOTSTART -eq 1 ]; then
service cribl start
else
${CRIBL_INSTALL_DIR}/bin/cribl start
ficurl Option
An easy way of wrapping HTTP methods is to use the curl command. Here is an example, which uses a GET operation by default, with the same URL used in the above HTTP example:
curl http://<leader hostname or IP>:9000/init/install-worker.sh?token=79364d6e-dead-beef-4c6e-554445664867Check Requirements above to avoid/resolve port or ownership issues.
Chaining Script Execution
The GET and curl procedures above will only output the contents of the script that needs executing - the script will still need to be manually executed.
However, you can automate that part, too, using a command like the one shown below. This passes the script’s contents to the bash shell to immediately execute.
curl http://<leader hostname or IP>:9000/init/install-worker.sh?token=79364d6e-dead-beef-4c6e-554445664867 | bash -As noted above, on Ubuntu and similar systems, you might need to insert sudo before the bash. If you don’t have a bash shell available, you can pipe the command to | sh - instead.
Adding Download URL
By default, the script gets configured to download the Cribl Stream package from the public Cribl repository. If you want to specify a different download location in the script, you’ll use the download_url parameter.
To successfully execute the curl command while also specifying the download URL, you must enclose the URL in double quotes. The reason for this is that the & character that joins multiple HTTP parameters is interpreted by the shell as the operator to run commands in the background. Double-quoting the URL, as shown in this example, prevents this.
curl "http://<leader hostname or IP>:9000/init/install-worker.sh?token=79364d6e-dead-beef-4c6e-554445664867&download_url=https://<your_internal_webserver>/cribl-2.2.0-4589617e-linux-x64.tgz" | sh -curl Offline Option
To bootstrap Workers in an internet-disconnected (e.g., airgapped) environment, you can separate downloading the installation package from Cribl’s repository versus running the curl command. Here’s an example:
Download the installation package from Cribl’s download page and place it in the desired directory, such as
/tmpor/root.Bootstrap the Worker from the file’s current directory using the following command. Replace
<CRIBL_FILE>with the full file name of the downloaded package, such ascribl-4.10.1-45136dbb-linux-x64.tgz:
curl "https://<mycriblleader.mydomain.ext>:9000/init/install-worker.sh?group=default&token=JOINTOKEN&download_url=file:///<CRIBL_FILE>&user=cribl&install_dir=/opt/cribl" | bash -Tagging to Assign Workers to Worker Groups
Cribl Stream uses Mapping Rulesets to map Workers to Worker Groups. When you create a Worker from a bootstrap script, you can take advantage of Mapping Rulesets to specify which Worker Group you want the newly-created Worker to join. This is done by adding tags to the download URL, in the form &tag=tag1&tag=tag2.
Basic Example
Suppose you have a Worker Group, Group420, that you want bootstrapped Workers to join.
In the active Mapping Ruleset for Group420, create a new rule that maps any Worker with the tag awseast1 to the Group420 Worker Group. You can do this with a filter:
cribl.tags.include('awseast1')Then, in the bootstrap script, add a download URL with a tag that matches the filter you just created. For example:
curl "http://<logstream_leader>:9000/init/install-worker.sh?tag=awseast1&token=criblmaster" | bash - When you use the script to bootstrap a new Worker, the Worker will be assigned to Group420.
Advanced Example
Suppose you have four Worker Groups distributed between two regions and two platforms:
| AWS | Azure | |
|---|---|---|
| Region 1 | Group01 | Group02 |
| Region 2 | Group03 | Group04 |
Using two tags (one for region and one for platform) you can represent all four possible combinations, and thus all four Worker Groups:
tag=aws&tag=region1maps toGroup01.tag=azure&tag=region1maps toGroup02.tag=aws&tag=region2maps toGroup03.tag=azure&tag=region2maps toGroup04.
For each Worker Group, you’ll create a Mapping Rule with a filter for the appropriate tag combination to match. For example, this filter would match Group04:
cribl.tags.includes('azure') && cribl.tags.includes('region2')Then you can use the tag combination in the download URL of a bootstrap script. For example, the tags in this download URL map to Group04:
http://<logstream_leader>:9000/init/install-worker.sh?tag=azure&tag=region2&token=criblmaster Any Worker created by the script with the above download URL will be assigned to Group04.
Status Codes
| Status Code | Reason |
|---|---|
| 200 - OK | All is well. You should have received the script as a response. |
| 403 - Forbidden | Either the node is not configured as a Leader, or the token provided is invalid. |
Restrictions
Keep the following in mind when using bootstrap scripts:
- Each Worker must normally have access to the internet in order to download the Cribl Stream installation binary from cribl.io. Where this isn’t feasible, you can use the
download_urlswitch to point to a binary in a restricted location. - TLS is not enabled by default. If enabled and configured, access to this feature will be over
httpsinstead ofhttp. - Red Hat, Ubuntu, CentOS, and Amazon Linux are the only supported Worker platforms.
User Data
For public-cloud customers, an easy way to use bootstrap scripts is in an instance’s user data. First, be sure to set the Leader Node to mode = 'leader'. Then use the following script (changing the command as needed. based on the information above). Upon launch, the Worker Node will reach out to the Leader, download the script, download the Cribl Stream package from the specified location, and then install and configure Cribl Stream:
#!/bin/bash
curl http://<leader-node-ip/host-address>:9000/init/install-worker.sh?token=<auth-token> | sh -




