These docs are for Cribl Stream 4.7 and are no longer actively maintained.
See the latest version (4.16).
Common Errors and Warnings
This page lists common error and warning messages that you might find in Cribl Stream’s internal logs and/or UI. It includes recommendations for resolving the errors/warnings. Messages are grouped by component (Sources, Destinations, and so on).
Whole message texts are not listed in every case. They may have different capitalization than the messages you may encounter in the product.
Where events are written to log files, they might reside in different logs variously devoted to data processing, cluster communication, or the REST API. (For details, see Types of Logs.) We note the log type where necessary.
NodeJS serves as the Cribl Stream backend and has a large collection of well documented errors of its own. Some of system-level are listed below with the appropriate action to take. The remainder are documented at https://nodejs.org/api/errors.html, specifically in the
Common system errorssection of that page.
Web UI
Duplicate GUID
When you deploy and first run Cribl Stream software, it generates a GUID (globally unique identifier) and stores it in a .dat file located in CRIBL_HOME/local/cribl/auth/. For example:
# cat CRIBL_HOME/local/cribl/auth/676f6174733432.dat
{"it":1570724418,"phf":0,"guid":"48f7b21a-0c03-45e0-a699-01e0b7a1e061"}When deploying Cribl Stream as part of a host image or VM, be sure to remove this file, so that you don’t end up with duplicate GUIDs. The file will regenerate on the next run.
“Failed to fetch”
Occurs only when accessing Data > Collectors. It can occur with ad blockers, or in the Brave browser (because the newly loaded page’s URL includes the string collector).
Recommendation
If you have an ad blocker, allowlist the https://<hostname>:9000/jobs/collectors (single-instance) URL or the https://<leadernode>:9000/m/<group_name>/jobs/collectors (Leader) URL.
“No workers registered”
Occurs during a live data capture, when there are no Workers available to fulfill the capture request. This error can be triggered if you attempt to capture events too quickly following a commit & deploy.
Recommendation
If you recently committed and deployed changes, wait 30 seconds and retry the live capture.
Navigate to Manage > Workers and confirm there are Workers currently registered with the Leader. Note that the error appears on a per-Group basis, which means that even if you have Workers registered, they may not be in the Group you’re capturing live data from.
“The Config Helper service is not available…”
Full Text: “The Config Helper service is not available because a configuration file doesn’t exist or the settings are invalid. Please fix it and restart Cribl server.”
Occurs only on Leader Nodes. Each Worker Group relies on a config helper process that runs on its behalf on a Leader Node, and that process is not currently running. This error is usually triggered by restarting Cribl Stream on the Leader Node, and then trying to access one of these UI features before the Cribl Stream server is fully up:
- Groups or Configure link (3.x).
- Worker Groups menu (2.x).
- Manage > Groups or Manage > Workers tabs (4.x).
Recommendation
Try again in a few seconds. If you’ve made changes to the backend or filesystem permissions, stop Cribl Stream, and make sure the cribl user owns all relevant assets, before restarting: sudo chown -R cribl.cribl /opt/cribl
“KMS saved, but secret exists in destination location. No data was migrated.”
This will appear when you attempt to save KMS Settings with a Secret Path entry that references a secret that already exists in HashiCorp Vault. It can also occur with OpenID Connect remote authentication. Cribl Stream has aborted the remote write to avoid overwriting an external shared secret.
Recommendation
Edit the Leader Node’s kms.yml file to use provider: local. Then restart Cribl Stream to correct the path conflict.
“The number of Worker Processes has been limited by the license.”
Workers use their local license until they connect to the Leader and download their current license data, which is why the message appears in Logs.
Recommendation
Ignore the message. Once the Worker checks in with the Leader and receives the production license, the rest of the Workers will start.
Sources
Below are listed general errors that can occur with many Sources. When you encounter a problem with a specific Source, check the “Troubleshooting” section in its documentation as well for potential solutions.
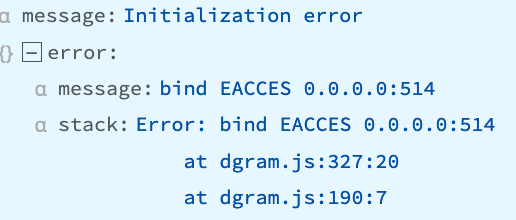
“bind EACCES 0.0.0.0:514”
Cribl Stream doesn’t have proper privileges to bind to the specified IP and port. Usually, this simply indicates that Cribl Stream is running as a non-root user, but a Source was accidentally configured to use a privileged port below 1024.
Recommendation
Check your Cribl Stream Sources’ configuration. The error’s channel field will indicate which input is affected. If you choose to enable access to the port range below 1024, see our configuration instructions for systemd and initd.
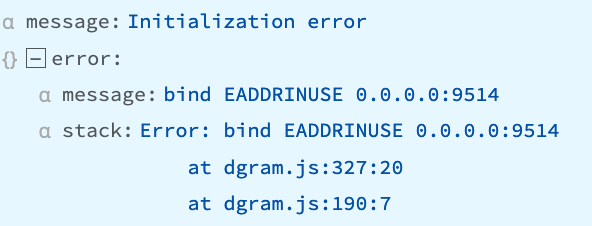
“bind EADDRINUSE 0.0.0.0:9514”
The interface and port combination is already in use by another process, which might or might not be Cribl Stream.
Recommendation
Check your Cribl Stream Sources’ configuration. The error’s channel field will indicate which Source is affected, but this error means that one or more other inputs are also using the same IP/port combination.
Destinations
Below are listed general errors that can occur with many Destinations. When you encounter a problem with a specific Destination, check the “Troubleshooting” section in its documentation as well for potential solutions.
“Sending is blocked”
The Destination is blocking. This can occur with any TCP-based Destination, and is logged only after 1 second of blocking. This can also occur between Worker and Leader when the Worker can’t connect to the Leader Node to send metrics data. When triggered by cluster communication, the warning will be in the Worker’s API log.
“Begin backpressure” and “end backpressure”
The Destination is blocking. Like the “sending is blocked” message, “begin backpressure” is logged only after 1 second of blocking. It is logged only once while backpressure is occurring (at the start), and it will always be followed by the “end backpressure” message.
TLS
“Certificate has expired”
Validate server certs or Validate client certs is enabled, and the peer’s certificate has expired.
Recommendation
Disable Validate server certs or Validate client certs (depending on whether Cribl Stream is serving as the client or server), so that encryption can still occur without authentication. Or renew the expired certificate.
“Client network socket disconnected…”
Full Text: “Client network socket disconnected before secure TLS connection was established”
Typically caused by a TLS protocol version mismatch between the client and server.
Recommendation
Verify that client’s and server’s TLS settings use the same minimum/maximum TLS version.
“Unable to get local issuer certificate”
Client can’t validate the server certificate’s CA (that is, the issuer) because it doesn’t trust the CA certificate. Or vice versa (server can’t validate client’s certificate CA) if mutual auth is enabled.
Recommendation
The CA certificates used by the server’s leaf certificate must be trusted by the client. See Configuring CA certs.
“Self signed certificate”
The client or server was presented with a self-signed cert from the peer, but that cert is not trusted.
Recommendation
The self-signed certificate must be trusted by the peer to which it’s presented. See Configuring CA certs.
“Hostname/IP does not match certificate’s altnames”
Full Text: “Hostname/IP does not match certificate’s altnames: host: <server hostname> is not in the cert’s list” or: “Hostname/IP does not match certificate’s altnames: IP: <server IP> is not in the cert’s list”
The server’s hostname/FQDN used on the client is not found in the CN or SAN attribute of the server’s certificate.
Recommendation
Examine the CN and/or SAN attribute, to see which names are listed that can be used as the server hostname/FQDN on the client. CN values with spaces are not supported as hostnames/FQDNS. If there isn’t a SAN attribute, then a new cert will need to be issued.
“No protocols available”
Full Text: “140244944713600:error:141E70BF:SSL routines:tls_construct_client_hello:no protocols available:”
The highest TLS protocol available by the client is still too low for the server to support.
Recommendation
Review the minimum/maximum TLS version settings on the client and server, to ensure that they overlap.
“Wrong version number”
Full Text: “140251374995328:error:1408F10B:SSL routines:ssl3_get_record:wrong version number”
The client is using TLS but the server is probably not configured for TLS.
Recommendation
Review the TLS settings on the server.
Pipelines/Functions
These events will be in the Worker Process logs.
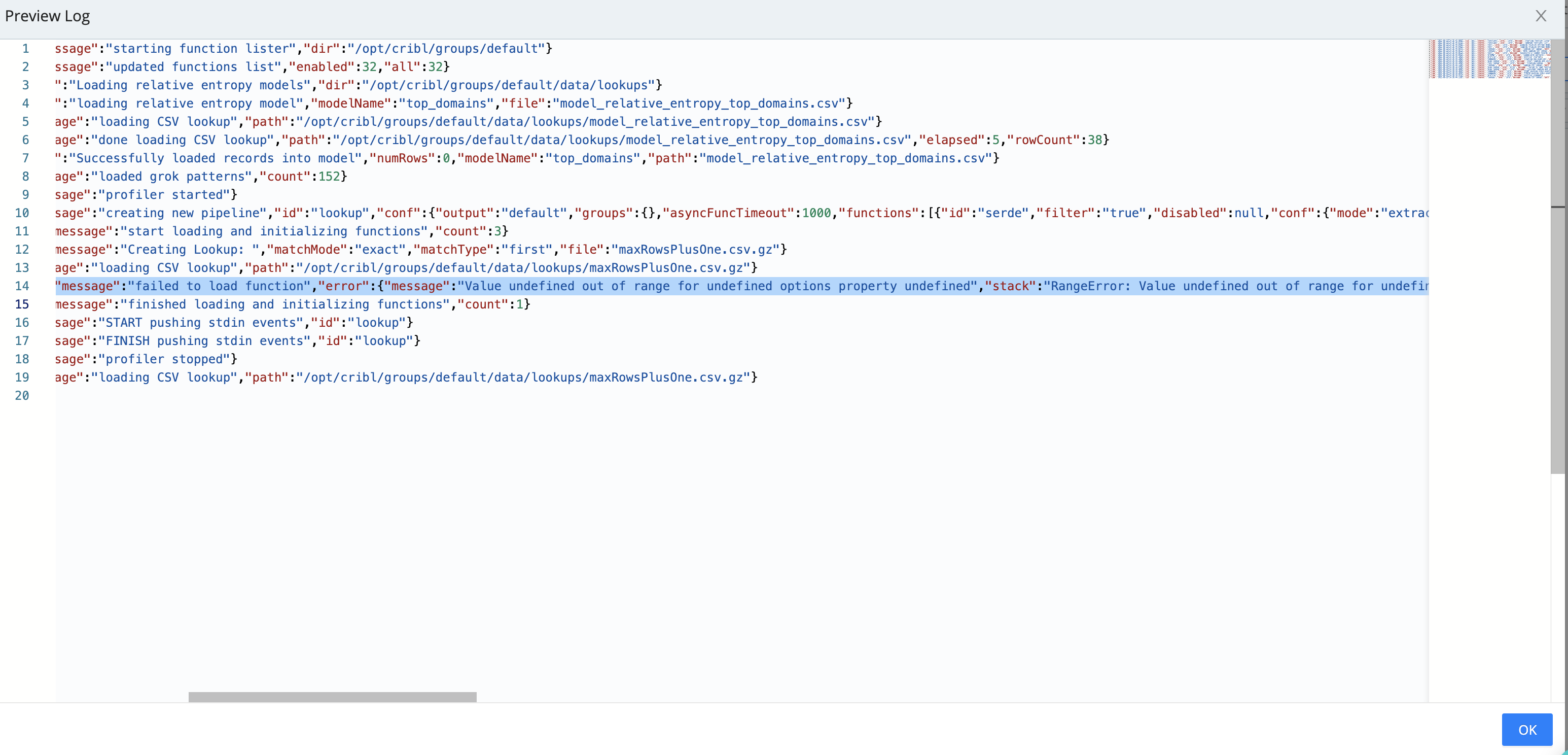
“Failed to load function…Value undefined out of range…”
A Lookup Function attempted to load a Lookup table that exceeded Node.js’ hard size limit of 16,777,216 (that is, 224) rows.
Recommendation
Split the Lookup table to smaller tables, or use the Redis Function.
Diag Command
“You are running Cribl Stream CLI as user=root…”
Full Text: “WARNING: You are running Cribl Stream CLI as user=root, while the binary is owned by the user=cribl. This may change the ownership of some files under CRIBL_HOME=/opt/cribl. Please make sure all files under CRIBL_HOME=/opt/cribl are owned by the user=cribl.”
This is caused by improper ownership on $CRIBL_HOME, and will cause some files to be missing from the diag.
Recommendation
Execute the chown command on the entire $CRIBL_HOME directory, so that everything can be owned by the proper user. Afterward, run the ./cribl diag create command again.
Distributed Deployment
“Access denied”
The Worker’s authtoken (located in $CRIBL_HOME/local/_system/instance.yml) is missing or doesn’t match the Leader’s.





